1. Introduction
The fluctuation in the cost of fuel prices, the increasing dem and for energy, and the evident signs of climate change, have fostered the development of technologies that utilize renewable energy sources. Concentrated solar thermal systems continue to be one of the most attractive options to produce power to meet utility-scale needs in certain regions of the U.S. However, in order to reduce levelized cost of solar power, solar thermal systems that can operate at higher temperatures, i.e. 450-600 °C, while remaining thermally stable, are needed.
Previous studies have based improvements of solar thermal system performance by configuring the structure of solar collectors, adjusting the selective coating for higher absorptivity, or preventing heat loss from the collectors. More recently, studies have based improvements of solar thermal systems performance by experimenting with different working fluids such as ammonia, air, silicon oil and organic working fluids. However, there are downfalls to using these fluids. Working fluids, such as CFC113, CFC114 and CFC11 can deplete the ozone layer [1], so they have been phased out. In addition, ammonia is a health hazard, air has poor thermophysical properties, and silicon oil's high viscosity made it difficult to h and le at low temperatures.
There are a few studies that have been conducted considering carbon dioxide(R-744)as the working fluid. Carbon dioxide has a high volumetric capacity, heat transfer coefficients tend to be higher than for other fluids, it is readily available, and it is thermally stable for a wide range of temperatures. Carbon dioxide has a critical pressure and temperature of 7.38 MPa and 31.1 °C, respectively, which is lower than other working fluids. In addition, it is abundant in nature, non-toxic, non-flammable and environmentally safe. This makes carbon dioxide a good c and idate for a working fluid in advanced solar thermal systems [1,2,3,4]. CO2 is a greenhouse gas when released to the atmosphere but its global warming potential index is far lower than other working fluids.
Non-imaging-optics based external compound parabolic concentrating reflectors(XCPC)combined with evacuated-tube collectors featuring a metal absorber and a glass-to-metal seal have been shown to obtain efficiencies higher than 40 % operating near 200 °CC without the need of tracking [5,6]. However, these results have been obtained using thermal oil(Duratherm 600) and there is very little information of the performance using alternative working fluids such as CO2. Yamaguchi et al. [2] carried out an experimental study of solar energy powered Rankine cycle using supercritical CO2. They found an estimated power generation efficiency of 0.25 and heat recovery efficiency of 0.65.
For higher temperatures, parabolic trough concentrators(PTC)with an absorber inside an evacuated-tube have been simulated and experimentally tested with operating temperatures up to 400 °CC using thermal oils such as silicon oil, biphenyl/diphenyl ether(VP-1) and Syltherm 800. Temperatures up to 500 °C have been reached using steam [7,8,9,10]. Above 400 °CC, the properties of thermal oils degrade significantly causing molecular bond breakdown, excessive system pressure, and an increase in viscosity that can reduce heat transfer efficiency [7,11]. In addition, thermal oils can be costly and dangerous due to their high flammability and toxicity [7,9]. Steam as working fluid produced equivalent results compared to thermal oils, however, water can only be used above 0 °CC and has to be operated under high working pressure.
This paper presents numerical simulations of XCPC and PTC collectors operating with CO2 as a working fluid for a range of temperatures that covers the medium and high range.
2. Medium Temperature: XCPC
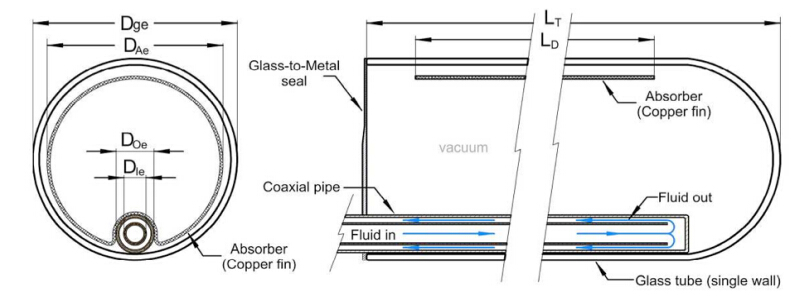
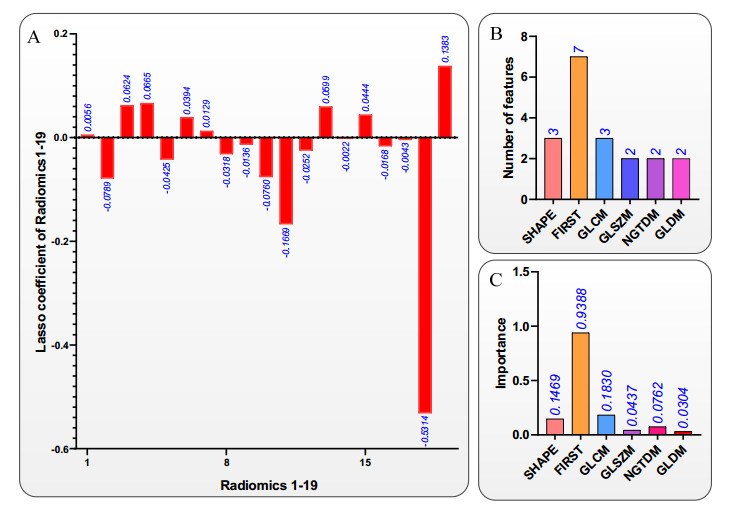
The mathematical model of the XCPC used to simulate the performance of CO2 under medium temperatures followed the analysis performed by Tovar-Fonseca [12]. A sketch of the XCPC concentrator and the evacuated tube collector is shown in Figure 1. The collector consists of a glass envelope that has a metal absorber inserted inside that acts as a fin contouring a coaxial pipe. A selective coating is applied to the exterior of the copper-fin absorber. One end of the glass tube is rounded, as shown in Figure 2, and the other end consists of a glass to metal seal that is used to ensure that the vacuum inside the glass tube is not lost. The coaxial pipes consist of concentric external and internal copper pipes with the inlet fluid to the collector flowing in the interior pipe and the exit fluid flowing in the annulus formed in between the two pipes. The absorber fin and the external copper pipe are welded together, so the heat reaching the absorber fin is transferred by conduction to the external pipe that transfers the heat to the working fluid by heat convection. The input dimensions and properties used to simulate the XCPC collector are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Properties and Dimensions for XCPC with Metal Absorber.
| Component | Material | Symbol | Value |
| Glass tube | Pyrex 7740 | | |
| Outer diameter | | Dge | 65 mm |
| Inner diameter | | Dg | 61 mm |
| Thermal Conductivity | | kg | 1.4 W/m·K |
| Emissivity | | eg | 0.92 |
| Metal absorber/fin | Copper | | |
| Outer diameter | | DAe | 56 mm |
| Thickness | | t0 | 1 mm |
| Effective length | | LD | 1, 640 mm |
| Absorptivity | | aA | 0.95 |
| Emissivity | | eA | 0.01 |
| Selective coating | Metal aluminum nitride cermet | | |
| Thermal conductivity | | kA | 200 W/m·K |
| Coaxial pipes | Copper | | |
| External pipe, outer diameter | | DOe | 30 mm |
| External pipe, inner diameter | | Do | 26.6 mm |
| Internal pipe, outer diameter | | DIe | 8 mm |
| Internal pipe, inner diameter | | DI | 6 mm |
| Hydraulic diameter | | Dh | 3.5 mm |
| Thermal conductivity | | kCu | 320 W/m·K |
2.1. Mathematical Model of XCPC Collector
A mathematical model to represent the XCPC collector was implemented using the thermal analysis in [12,13] which was implemented in Engineering Equation Solver(EES)[14] to simulate the behavior of CO2 as the working fluid.
The following assumptions were made: uniform heat flux on absorber, incompressible fluid, constant properties of fluid, constant heat transfer coefficients, negligible fouling factor, negligible potential and kinetic energy changes, and fully developed conditions.
2.1.1. Evacuated Glass Tube
An energy balance applied to the glass cover is given by:
| αgGc+11εA+1−εgεg(DAe+t0Dg)σ(T4A−T4g)−h0(Tg−T∞)−εgσ(T4g−T4sky)=0
|
(1)
|
where αg is the absorption coefficient of the glass, and Gc is the irradiance incident on the metal absorber(Gc = Total irradiance incident on concentrator aperture × Concentration ratio = Gs × Cmax). TA is the temperature of the absorber, Tg is the temperature at the glass, T∞ is the temperature of the ambient air, and σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant. Tsky is the sky temperature and can be related to the ambient temperature by Tsky = 0.0552T∞1.5 [15]. h0 is the convection heat transfer coefficient between the outside exterior of the glass and the ambient air, and is given by the empirical equation: h 0 =2.8 + 3v, where v is the velocity of the ambient air nearby the surface of the exterior glass [12,15]. Finally, eg is the emissivity of the glass, eA is the emissivity of the absorber, DAe is the outer diameter of the metal absorber, Dg is the inner diameter of the external glass, and t0 is the thickness of the metal absorber.
2.1.2. Absorber
The energy balance applied to the absorber gives the following equation:
| αAτg1−(1−αA)ρgGc−11εA+1−εgεg(DAe+t0Dg)σ(T4A−T4g)−q″cond=0
|
(2)
|
αA is the absorptivity of the absorber, and τg and ρg are the glass transmissivity and reflectivity, respectively. Performing an energy balance at the absorber fin, the expression for the temperature of the fin as a function of the arc length is given by
| T−T∞−S/ULTb−T∞−S/UL=coshcosh(mx)coshcosh(mπDAe/2)
|
(3)
|
where S = κGs, m =
√(UL/t0/kA)
,
κ is the absorption coefficient of the absorber fin,
t0 is the thickness of the selective coating,
kA is thermal conductivity of the selective coating,
x is the arc length along the fin,
UL is the total loss coefficient, and
Tb is the temperature at the point of contact between the pipe and the absorber fin. The heat transfer by conduction at the point of contact between the fin and the pipe is calculated from Eq. 4,
| qcond=−kAAtmλtanhtanh(mπDAe/2)
|
(4)
|
where λ = Tb - T∞ - S/UL.
2.1.3. Pipe
The energy collected at the fin is transferred to the working fluid as:
where Tf =(Tin + Tout)/2, Tin, Tout is the inlet and outlet temperature of the fluid, respectively, and Rtotal is the resistance by conduction and convection at the pipe given by Eq. 6 for the XCPC.
2.1.4. Thermal Resistance
The total thermal resistance from the pipe to the fluid is as follows:
| Rtotal=lnln(DOe/Do)2πLDkCu+1πDOLDhfluid
|
(6)
|
where DO is the inner diameter of the external copper pipe, DOe is the outer diameter of the external copper pipe, LD is the length of the metal copper fin absorber, kCu is the thermal conductivity of copper, and hfluid is the convection coefficient of the working fluid. The outlet temperature can be obtained from
where Cp is specific heat of the working fluid, ∆T = Tout - Tin.
2.1.5. Efficiency
The efficiency, η, is calculated as,
where Age is the area of the external glass wall.
2.2. Validation
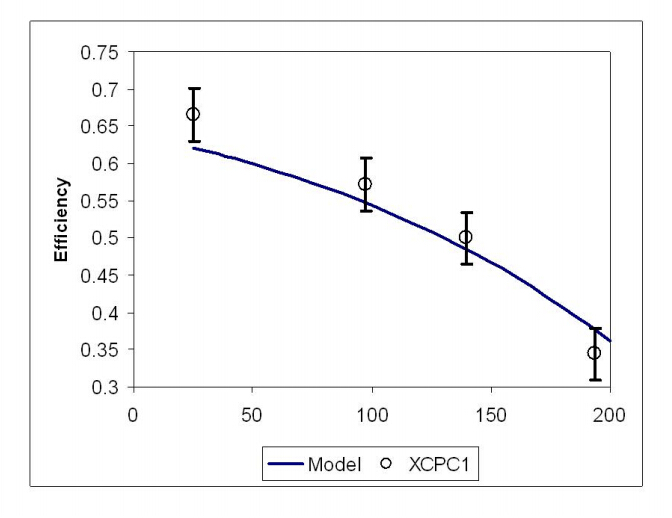
The numerical model was validated with XCPC collector test data obtained by Winston et al. [16,17] using Duratherm 600 thermal oil as the working fluid. Figure 3 shows the comparison of the thermal efficiency of the collector obtained from experimental data and numerical results for a range of inlet temperatures between 80 °C and 200 °C for a mass flow rate of thermal oil of 0.10 kg/s. The results agree reasonably well with the numerical model slightly under predicting the experimental data. Thus, by changing the thermophysical properties, it is possible to study the performance of such a collector using CO2 as the working fluid. Carbon dioxide does require the operation at high pressure but this paper intends to analyze the thermal performance of such a working fluid so no stress analysis has been performed to adjust pipe wall thicknesses.
3. High Temperature: PTC
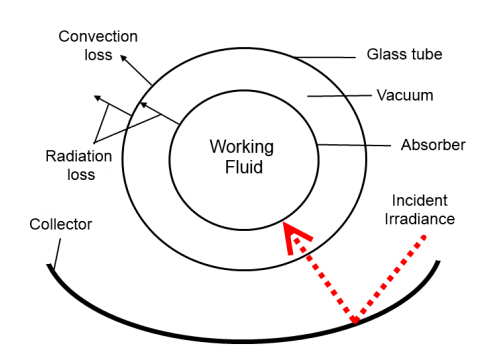
The concentration ratio, the effective aperture area to the glass area, is significantly higher in PTCs than in XCPC systems. The model used in this paper for the high-temperature parabolic trough concentrator with evacuated-tube absorber follows the analysis by Odeh et al. [7] which simulates the LS2 design developed by SEGS(Solar Thermal Electric Generation Systems). The evacuated-tube collector consists of a metal absorber concentric to a glass tube. Figure 4 depicts the cross-sectional view of the assembly. The working fluid directly flows from one end of the metal absorber tube to the other, i.e. single-pass configuration. The metal absorber in this model is made from steel with a total length of 99 meters. This total length is composed of 4-meter long collectors connected in series with metallic bellows at each end, to allow for the expansion of the metal absorber. The annulus between the glass tube and steel absorber is under vacuum and the external surface of the absorber pipe is covered with a selective coating. Input dimensions and parameters for PTC model are presented in Table 2.
Table 2.Properties and Dimensions for PTC with Evacuated-Tube Absorber
| Component | Symbol | Value |
| Glass tube | | |
| Outer diameter | Dge | 115 mm |
| Inner diameter | Dg | 109 mm |
| Thermal conductivity | kg | 1.4 W/m∙K |
| Emissivity | eg | 0.90 |
| Evacuated-tube steel absorber | | |
| Outer diameter | DAe | 70 mm |
| Inner diameter | DA | 66 mm |
| Effective length | LD | 99 mm |
| Absorptivity | αA | 0.906 |
| Selective coating | | |
| Thermal conductivity | kA | 54 W/m∙K |
| Thickness | t0 | 1 mm |
3.1. Mathematical Model of PTC
The mathematical model was implemented in EES to simulate the performance of the PTC with the metal pipe inside an evacuated-tube as described in Odeh et al. [7].
3.1.1. Glass Tube
The total heat loss of the glass tube, considering radiation from the glass to the sky, convection from the glass to the surrounding air, and heat loss from the bellows, is given as:
| qtotal,glass=σεg(T4g−T4sky)Age−h0(Tg−T∞)Age−Abh0(TA−T∞)ηb=0
|
(9)
|
where Ab is the exposed surface area of the bellows, ηb is the bellows fin efficiency which is estimated to be 70 %, and Tsky is adapted from [18] and approximated to be:
3.1.2. Absorber
The total heat loss of the absorber due to radiation exchange between the absorber and glass and the convection from the bellows is:
| qtotal,absorber=σ(T4A−T4g)1εAAA−DAeDg(1/εg−1)−h0(TA−T∞)ηb=0
|
(11)
|
where the emissivity of the absorber, εA is defined as,
| A=0.00042×Twall−0.0995
|
(12)
|
and Twall is the absorber wall temperature. Since we are assuming that the annulus, space between the glass and the absorber, is a perfect vacuum, the heat loss by conduction of the residual gas in the annulus is neglected. The energy from absorber is transferred to the working fluid as:
| qfluid=TA−TfluidRtotal
|
(13)
|
where Tfluid is the temperature of the fluid and Rtotalis the resistance by conduction and convection of the PTC given by Eq. 14.
3.1.3. Thermal Resistance
The thermal resistance from the absorber pipe wall to the fluid has been calculated as follows:
| Rtotal=lnln(DAE/DA)2πLDkA+1πDALDhfluid
|
(14)
|
3.1.4. Efficiency
The efficiency formulation is obtained with the correlation provided by Odeh et al. [12]. The heat loss is given as
| q=(a+c·v)·(TA−T∞)+εA(T4A−T4sky)
|
(15)
|
where v is the wind velocity, and a, b, and c are coefficients. This formulation was developed to fit the LS2 collector type. This heat loss formulation is convenient since it depends solely on wind speed, absorber temperature, and ambient temperature. From S and ia National Laboratory testing on the LS2 collector, the parameters are a = 1.9182 × 10-2 W/m2∙K, b = 2.02 × 10-9 W/m2∙K-4, and c = 6.612 × 10-3 J/m-3∙K. The efficiency formulation can be expressed in terms of the heat loss formulation from Eq. 15. The development of the efficiency formulation is in terms of absorber temperature rather than working input temperature in order to consider performance of other working fluids. The efficiency is given by:
| η=ηopt·Kτα−(a+c·v)·TA−T∞I−εA·b·T4A−T4skyI
|
(16)
|
where ηopt is the optical efficiency of the collector, I is solar irradiance, and Kτα is the incident angle modifier. From LS2 collector tests ran by Dudley et al. [19], ηopt is given as 73.3 % where incident angle modifier is
| Kτα=coscos(θ)+0.000994(θ)−0.00005369(θ)2
|
(17)
|
where θ is the beam incidence angle to the collector normal.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. XCPC
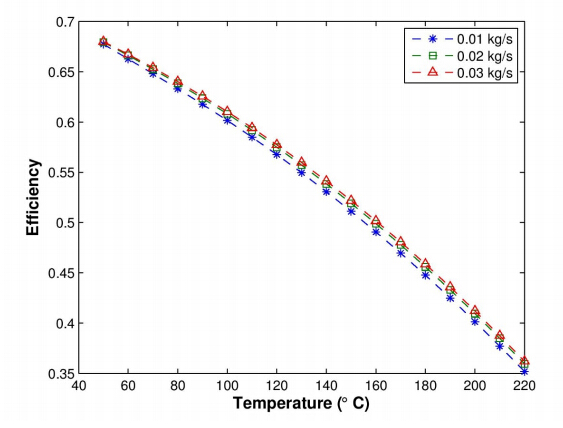
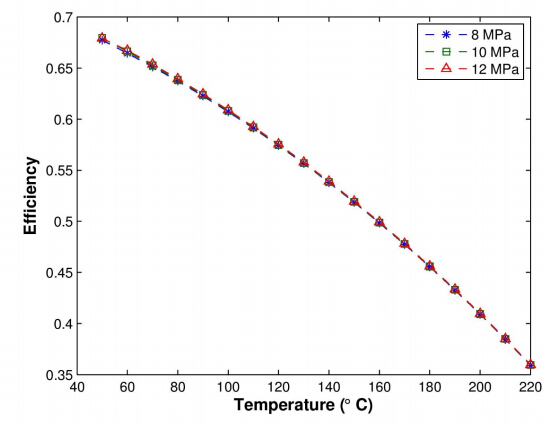
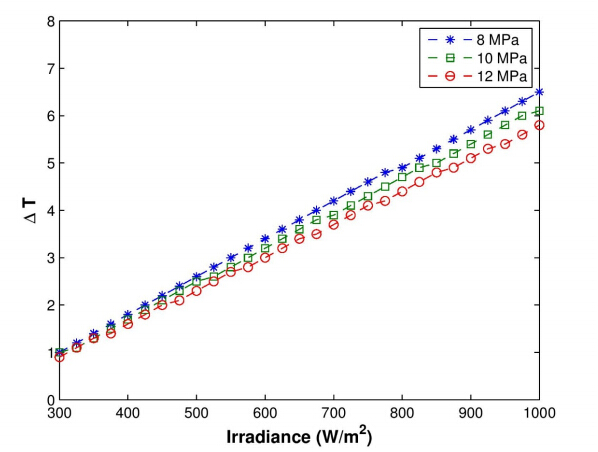
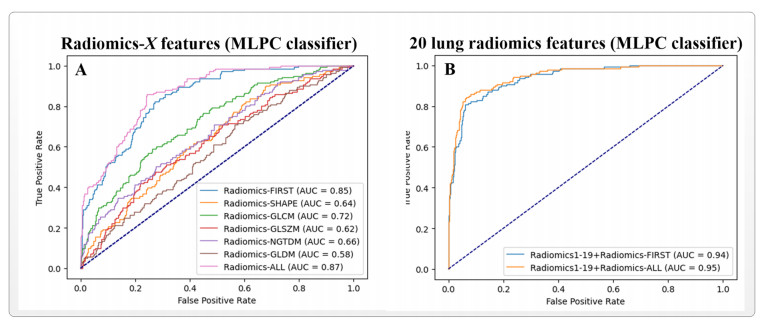
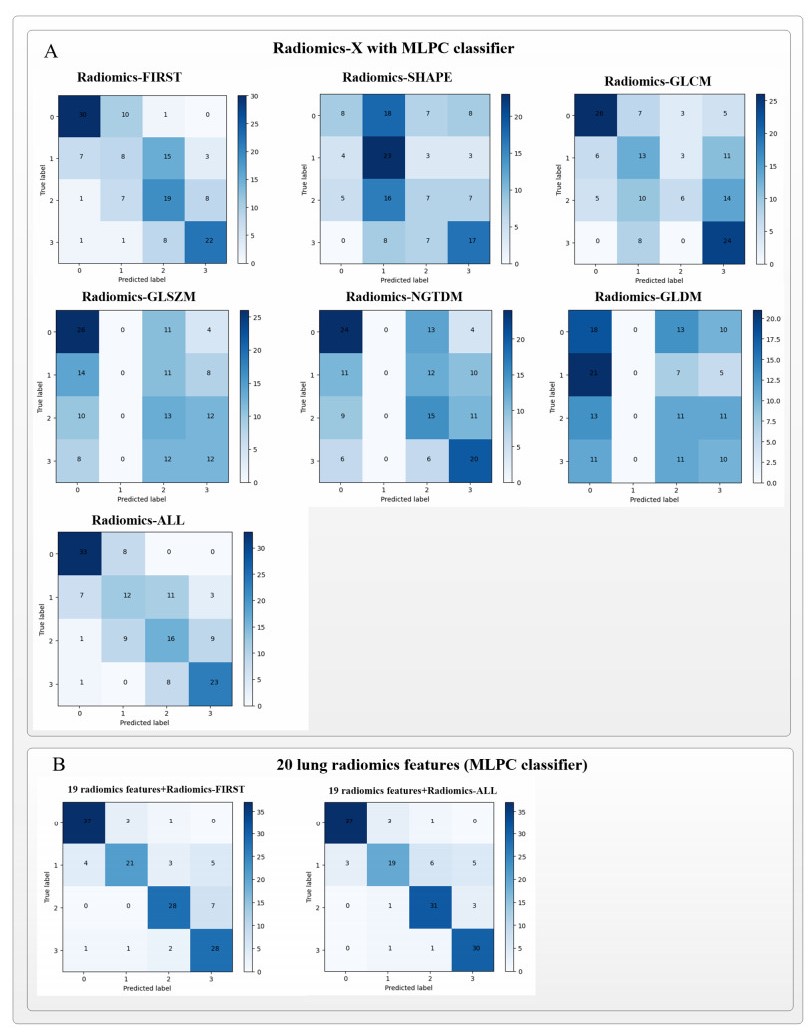
Three cases were simulated to assess the performance of CO2 as the working fluid in the XCPC collector with a metal absorber. The ranges of values used for the operating parameters in the model are provided in Table 3. The first case analyzes the thermal efficiency of the collector as a function of working fluid inlet temperature for the range between 50 °C and 220 °C at three different mass flow rates(0.01, 0.02, and 0.03 kg/s). Figure 5 shows that efficiencies higher than 40 % can be obtained at operating temperatures near 200 °C. It is observed that the thermal efficiency is not a strong function of the mass flow rate for the range of values considered in this simulation. The second case, presents the analysis of the thermal efficiency as a function of inlet temperatures of CO2 at three different operating pressures, i.e. 9, 10, and 12 MPa. Figure 6, shows that the effect of operating pressure on the thermal efficiency is negligible for the three values of operating pressures modeled. Further reduction in pressure will cause a significant reduction in density of the working fluid so very high flow velocities would be required to maintain a fixed mass flow rate. Lastly, the third case analyzes the effect of solar irradiance on the difference between outlet and inlet fluid temperature(∆T = Tout - Tin)to the collector. Solar irradiance covers the range between 300 and 1, 000 W/m2 for three different pressures(8, 9 and 10 MPa). Figure 7 indicates that ∆T varies linearly with solar irradiance for the range of values considered in this simulation. A reduction in operating pressure decreases the density of the working fluid resulting in a larger temperature difference, especially at high values of solar irradiance.
Table 3.XCPC - Simulated Cases
| Case 1: Efficiency vs. input temperature at different flow rates |
| Parameter | Range/Values |
| Temperature | 50 °C to 220 °C |
| Flow rate,
⋅m
| 0.01, 0.02, 0.03 kg/s |
| Solar irradiance | 900 W/m2 |
| Case 2: Efficiency vs. input temperature at different pressures |
| Parameter | Range/Values |
| Temperature | 50 °C to 220 °C |
| Pressure, P | 8, 9, 10 MPa |
| Solar irradiance | 900 W/m2 |
| Case 3: ∆T vs. solar irradiance at different pressures |
| Parameter | Range/Values |
| Solar irradiance | 300 - 1000 W/m2 |
| Pressure, P | 8, 9, 10 MPa |
| Inlet temperature | 150 °C |
4.2. PTC
The analysis compares the overall heat loss of Syltherm 800 thermal oil and CO2 for a range of fluid temperatures above ambient, i.e. Tfluid - T∞. The ranges of values used for the operating parameters in the model are provided in Table 4. Because of the properties of Syltherm 800, the maximum physical operable temperature is 400 °C. From Figure 8, it is seen that below 400 °C, the heat loss using CO2 is comparable to Syltherm 800 at the same mass flow rate of 0.8 kg/s. The main difference is that the thermophysical properties of CO2 remain stable so the simulation can be extended to a range of ∆T near 600 °C. Due to the high operating pressure, it is desirable to minimize the CO2 charge on the system. Thus, it is of interest to study the effect of lower mass flow rates on the total heat loss. Figure 8, shows total heat loss as a function of CO2 mass flow rate for 0.8 kg/s, 0.2 kg/s and 0.08 kg/s. It is observed that at 600 °C above ambient temperature, the total heat loss for the CO2 system increased approximately 10 % at 0.2 kg/s and 20 % at 0.08 kg/s compared to the heat loss at a mass flow rate of 0.8 kg/s.
Table 4.PTC - Simulated Case
| Heat loss vs. ∆T for CO2 and Syltherm 800 |
| Tfluid - T∞ | CO2: 50 °C to 600 °C, Syltherm 800: 50 °C to 400 °C |
| Flow rate,
⋅m
| CO2: 0.08, 0.2, and 0.8 kg/s, Syltherm 800: 0.8 kg/s |
| Pressure, P | CO2: 12 MPa |
| Solar irradiance | 1000 W/m2 |
5. Conclusions
In this study, two models of solar thermal collectors were implemented to analyze the performance of CO2 as a working fluid. The model of the XCPC with metal absorber, for medium operating temperatures, shows that thermal efficiencies comparable to thermal oils can be achieved using CO2 as the working fluid. The main drawback is the high operating pressure needed. For the model of the PTC with evacuated-tube absorber, for high operating temperatures, the heat loses using CO2 were also comparable to the ones obtained using Syltherm 800 but due to the thermal stability of carbon dioxide, a much larger range of fluid temperatures above ambient can be analyzed.
Acknowledgments
This project has been partially funded by the California Energy Commission, Contract#: POEF01-M04.
Nomenclature
Age Area of the external glass wall, [m2]
At Cross-sectional area of the absorber fin, [m2]
Cmax Concentration ratio of reflectors
Cp Specific heat of working fluid, [J/kg∙K] DA Inner diameter of the metal absorber, [m]
DAe Outer diameter of the metal absorber, [m]
Dg Inner diameter of the glass tube, [m]
DO Inner diameter of the external pipe, [m]
DOe Outer diameter of the external pipe, [m]
Gc Total irradiance incident on the absorber, [W/m2]
GS Solar irradiance incident on concentrator aperature, [W/m2]
h0 Convection coefficient on outside of glass cover, [W/m2∙K]
hfluid Convection coefficient of working fluid, [W/m2∙K]
I Solar irradiance, [W/m2]
kA Thermal conductivity of the selective coating on the metal absorber, [W/m∙K]
kCu Thermal conductivity of copper pipe, [W/m∙K]
Kτα Incident angle modifier
LD Effective length of the absorber, [m]
.m
Mass flow rate of working fluid, [
kg/
s]
q Heat transfer, [W]
q” Heat flux, [W/m2]
Rtotal Total thermal resistance from the external wall of the pipe to the fluid, [m]
t0 Thickness of selective coating, [m]
T Temperature of working fluid, [K]
TA Temperature of absorber, [K] Tb Temperature of the fin at contact point with the external copper pipe, [K]
Tfluid Temperature of the working fluid, [K]
Tg Temperature of glass cover, [K] Tin Inlet temperature of working fluid, [K]
Tout Outlet temperature of working fluid, [K]
Tsky Temperature of atmosphere, [K]
Twall Absorber wall temperature, [K]
T∞ Tempreature of ambient air, [K]
v Wind velocity, [m/s]
x Arc length of absorber fin, [m]
Greek Symbols
αA Absorptivity of the absorber
αg Absorptivity of the glass
εA Emissivity of the metal absorber
εg Emissivity of the glass
τg Transmissivity of glass
ρg Reflectivity of glass
η Efficiency of the collectors
ηb Fin efficiency of the bellows
ηopt Optical efficiency of the collectors
κ Absorption coefficient of absorber fin









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: