1. Introduction
1.1. Background
International as well as national environmental and energy policies have resulted in a boost of bioenergy during the past two decades. Particularly in Germany the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), passed in 2000, and the so called ´energy transition´, which was initiated in 2011 have led to a significant expansion of renewable energy. Biomass plays an important role among the different sources of renewable energy. Since the late 1990s there was a strong tendency in Germany to expand the cultivation of energy crops which is shown by an increase of over 500% from 1997 to 2010 [1]. According to the 2006 action plan "Biomass" there is a potential for a share of 8-10 % in the national primary energy consumption [2]. The focus lies on biogas produced from silage maize or corn. For agriculture in rural areas the use of renewable energy products potentially creates an added value through new production and market alternatives.
Moreover, the substitution of fossil energy has positive effects on the balance of greenhouse gases [3], but at the same time, the intensification of agricultural production can lead to severe impacts on soil, groundwater [4,5] and biodiversity [6,7], which opens many conflicts concerning commitments of the European Union (EU) to maintain biodiversity and to protect surface and ground water [8,9].
Modeling approaches provide an important contribution to analyze the impact of increasing competition in the agricultural biomass production for food, feed and fuels. In order to be able to depict the diverse economic and ecological effects of agricultural production, integrated model approaches are necessary. During the past decades numerous approaches were developed for specific modelling levels, such as: farm, region, country, EU and global [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Against the background of ecosystem services used by agriculture Kirchner et al. [15] provide a very detailed overview on existing modelling approaches for the assessment and evaluation of economic, biotic and abiotic effects.
1.2. Objectives
Environmental impacts and conflicting nature conservation targets play a vital element in the actual debate on how much intensification can be still considered as a sustainable solution to meet food and energy demand. Restrictions on the share of energy crops or compensation for impacts by enforcing nature conservation measures represent key policies to control intensification and are considered in our study. We ask for their efficiency in a scenario experiment which is based on geographic information processing and numeric models and addresses the field of integrated land-use modelling. In contrast to Kirchner et al. [15], who considers land-use change under climate scenarios, our approach considers the effects of land-use decisions on biodiversity and soil degradation. And as a second question, we analyze economic, spatial and environmental effects from restrictions deduced from worthwhile nature conservation targets.
So the objective of the study is to support policy making by answering the following questions when facing intensification by biomass production for energy use:
- If there is an increase of using energy from biomass, which effects on farm production portfolio and farmer's income are to be expected?
- Which effects on soil erosion, nitrate leaching and greenhouse gas emissions are to be expected, which effects on biodiversity?
- Is there a target conflict between ability for intensification and ecological and environmental standards?
- Do restrictions on the availability of farm land from nature conservation reasons enable more sustainability?
These general questions are answered by a case study which is set up for the German federal state of Baden-Württemberg. The study suggests an integrated modelling approach (IMA) which implements a model chain and which is able to combine spatially aggregated economic optimization and spatially explicit ecological evaluation schemes. The approach tackles an ongoing challenge in economic-ecological modelling: to work on different spatial and time scales [12,18,19] including the choice of an appropriate method when linking models of different spatial scales which is of particular importance for the quality of modelling results [20,21].The applied methodology uses scenarios as defined by van Notten [22] and Sparrow [23] to quantify trade-offs and synergies between the expansion of area for the cultivation of energy crops and the target to protect ecosystem integrity and services.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Integrated modelling approach
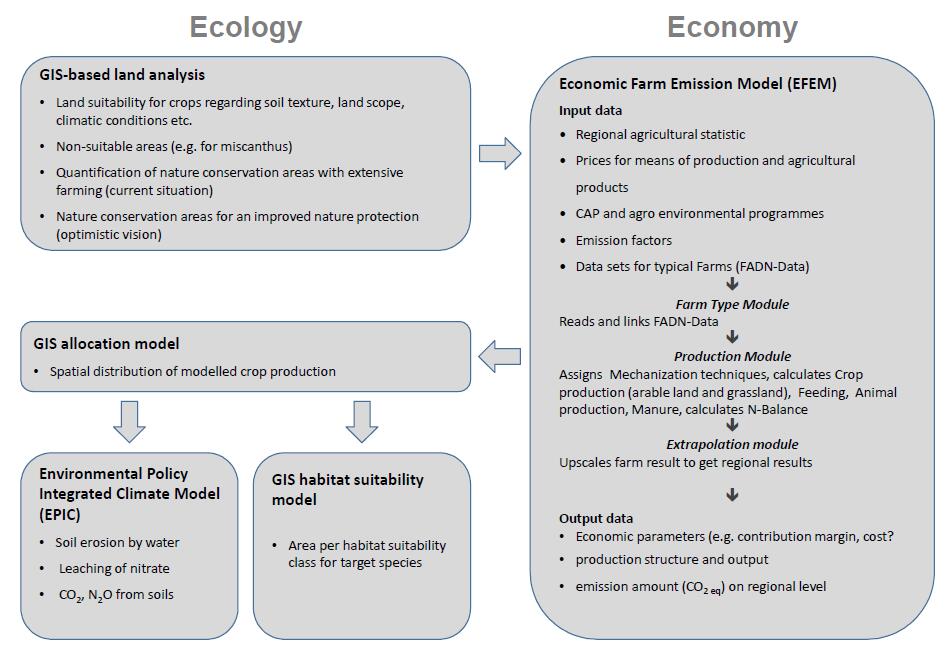
The integrated modelling approach (IMA) reported in this paper follows to the general idea (i) to calculate agro-economic parameters using an optimization approach that leads to spatially aggregated crop shares and (ii) to disaggregate the results at a spatially explicit 1-hectare (ha) raster level which sufficiently allows site specific calculations and balances of ecological effects. We followed a strategy of loosely coupling the different components of a model chain by file exchange when built up the IMA which is sketched in Figure 1.
The approach uses a comparative static linear optimization model called Economic Farm Emission Model (EFEM; see chapter 2.3) which maximizes total gross margins on farm level. The results from EFEM are subsequently analyzed in regard to ecological impacts at a spatially explicit level. For this purpose a spatial distribution model for cultivated crops is applied (see chapter 2.6). Environmental impacts on soil and water are reported following calculations from the Environmental Policy Integrated Climate model (Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC) (see 2.4). Impacts on species habitat on the other hand are analyses using a GIS approach (see 2.5).
2.2. Study area
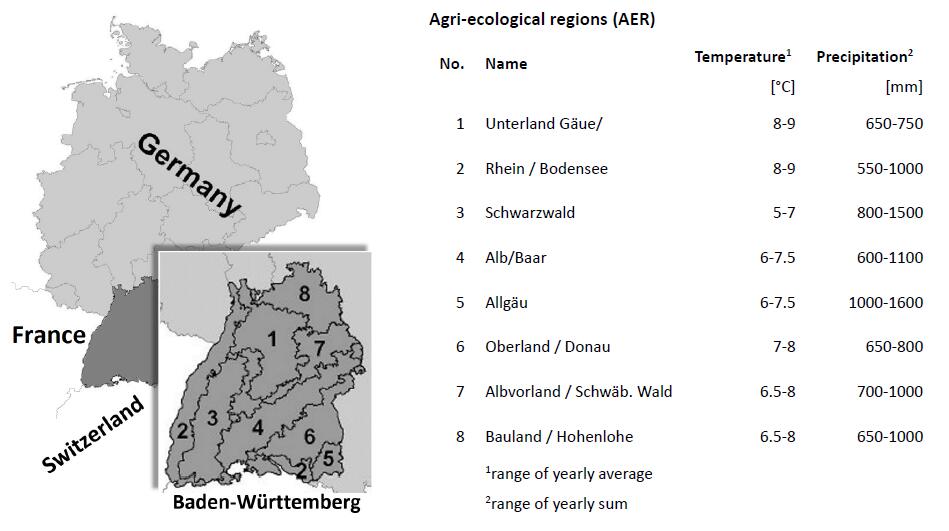
We applied the approach to the territory of the German Federal State of Baden-Württemberg on the basis of eight agri-ecological regions (see Figure 2). The regions are characterized by different agricultural production potentials due to a broad range of annual precipitation between 600 mm (minimum) and 1600 mm (maximum) per year, an average annual temperature between 5 °C (minimum) and 9 °C (maximum) and by different soil types. Predominant soil types in Baden-Württemberg are Cambisoles, haplic Luvisoles and Fluvisoles with mainly silty-loam but partly also sandy or clayey soil types. The utilized agricultural area (UAA) is about 14,000 km² (60%arable land and 40% grasslands) and covers 46% of the State territory.
2.3. Agricultural sector modelling
The economic-ecological model EFEM (Figure 1) is an agricultural sector model, follows a bottom-up approach and describes all predominant farming systems in Germany at farm and at regional scale. EFEM is a comparative static supply model that maximizes the gross margin at farm level based on linear programming [24,25]. The predominant farm models are classified according to the farm type systems of the EU classification scheme and derived by analyzing datasets of the Farm Accountancy Data Network "FADN" [26]. The capacities of typical farm models, such as stable places, farmland, labour ability etc., are the basis for the farm type module and restrict the linear optimization processes in EFEM. The prices for producers and for means of production and the production capacities for typical farms are exogenously determined.
The activities for crop and livestock production are integrated in the production module of EFEM. They differ regionally in terms of yields, intensities, revenues and costs. To clear annual variations, estimates for prices, yields and costs are based on an average of five years. The model includes all important agricultural production methods. Beside conventional production methods, environmentally friendly production methods for crop production and grassland cultivation that are supported by the agri-environmental programme of Baden-Württemberg (MEKA) are integrated in the model.
Grassland can be used for grazing or hay and grass silage production. Depending on the frequency of use, different fertilization intensities are formulated in the model. The yields of the different grassland management options are simulated with a model internal yield module, depending on the amount of fertilizer applied. In the field of bioenergy crop production, beside annual crops, perennial energy crops such as short rotational forestry plantations (willow, poplar) and miscanthus are taken into consideration. Some crops can be used as food or as feeding stuff or for energy production (Table 1). Based on the comparative static approach, crop rotations are specified as a maximum cultivation share for all crops as model restrictions. The grassland biomass can alternatively be used for biogas or animal production. Perennial energy crops are only used for the production of thermal energy.
Table 1. Utilization options and energy yields for the modelled crops (own calculations according to KTBL [27] and Öko-Institut [28])a.
| Food/Feeding
stuff | Bioenergy |
Biogas
plant | Combustion | Biofuel | Net energy
production |
| Crop | | | | | kWh/ha | kWh/t
DMc |
| Cerealsb | X | | X (only
straw) | | 20,407 | 34.5 |
| Winter rapeseed | X | | | X | 12,949 | 38.4 |
| Sunflower | X | | | | | |
| Sugar beet | X | | | | | |
| Potatoes | X | | | | | |
| Maize (corn, silage) | X | X | | | 29,382 | 19.1 |
| Clover grass | X | X | | | 25,345 | 18.2 |
| Grasslandd | X | X | | | 4270 | 18.1 |
| Miscanthus | | | X | | 61,966 | 33.0 |
Short rotation plantations
(willow, poplar) | | | X | | 31,930 | 27.9 |
a All values are exemplary for AER1
b Straw of all cereals cultivated in EFEM can be used. The values here are exemplary for winter wheat
c Dry matter
d Exemplary for a 3-cut grassland silage |
The modelled livestock production activities comprise dairy farming including heifers for restocking, male and female calves, fattening bulls, suckler cows, pig production (fattening pigs and sows) and poultry production (layer hens and broilers). EFEM considers all variable costs including machinery costs but not investment and fixed costs. Perennial crops are characterised by high initial costs and irregular revenues over long operation lengths. Therefore, the specific costs are amortised over the entire duration of operation and are considered as annual average costs in EFEM.
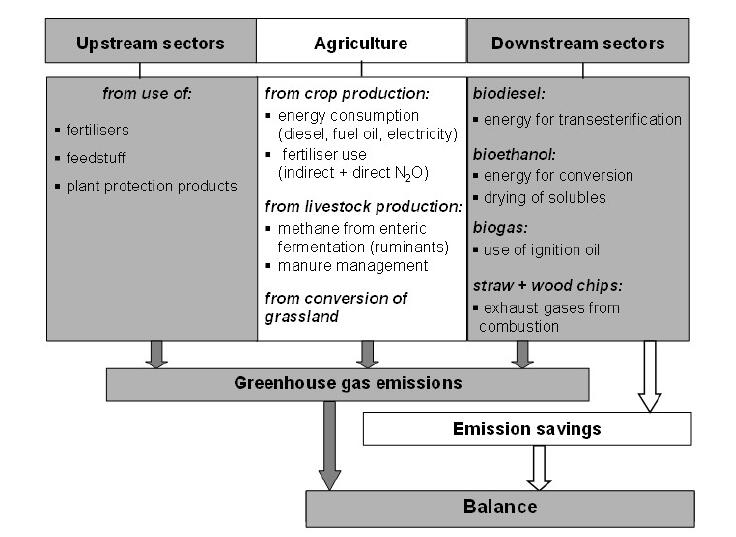
In the production module also greenhouse gas emissions from the agricultural sector are quantified. Thereby the emissions are distinguished according to their sources along the production process chain (Figure 3): upstream processes, agricultural production and downstream processes for the conversion of energy crops into bioenergy. In this way, the greenhouse gas balance shows the net substitution effect from agricultural bioenergy production, because the emissions of the conversion processes are taken into account [29]. Using global warming potential for 100 years the different greenhouse gases are added to CO2 equivalents (CO2e).
IMA works on eightagri-ecological regions as aggregated spatial units. They subdivide Baden-Württemberg into homogeneous regions regarding natural conditions for agriculture. This approach was chosen, because it allows identifying and distinguishing natural site conditions as well as it considers a sufficient number of predominant farms from the FADN data sets while assuring data privacy.
By linking the production module and the farm type module and subsequently performing the optimization process, agri-economic values like gross margin, factor input, amount and structure of agricultural production and associated environmental impacts at farm level were estimated. The results at farm level were extrapolated to regional scale with expansion factors that were identified by a linear optimization approach (extrapolation module), independently from EFEM. Thus upscaling factors are generated which help to cover the regional capacities of the six designated farm type models. A detailed description of this approach and of the EFEM is given in Schäfer [30].
For the scenarios EFEM analyses exclusively the supply side and not the overall agriculture biomass market. Therefore, a full elasticity of demand is assumed for the scenarios BioE1 and BioE2 (refer to Table 3). Consequently, biomass produced for energy generation completely finds a purchaser accepting the assumed prices.
EFEM was calibrated on the basis of statistical data for the reference year 2003. The calibration results showed a high accordance with the statistical data deviating for crop production of maximum 7% and for livestock production of maximum 3%, due to integrated restrictions for housing capacities.
2.4. Analysis of impacts on soil and water
By a geometrical intersection of land use (cultivated crops), associated climate station data and soil association layers, quasi homogeneous spatial entities were generated with a minimum area of 1 ha, the so-called Land Use Soil Association Climate (LUSAC) land units. As an input for LUSAC generation and properties assignment theSoil and Land Resource Information System (SLISYS) was applied [31]. SLISYS couplesGIS and the Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC models described below, documents soil and terrain data from 311 soil profiles in southwest Germany according to the international Soil and Terrain Database (SOTER) standard [32] to be mapped to the main mapping units of the general soil map in the scale 1:200,000, edited by the Geological State Office. Secondly LUSACs are generated from 20 climate stations for which daily values of temperature (minimum and maximum), precipitation and days of rain, air humidity, wind speed and global radiation are recorded.
Operating on SLISYS and concerning LUSACs the environmental cropping models in Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC (version 0509) [33,34] were applied for soil erosion by water(according to the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE)), for nitrate (NO3) leaching and for greenhouse gas emissions (CO2, N2O) from soils. The estimationsare based on climate parameters and soil properties and depend on different field management systems.CO2 soil emissionwas calculated based on the change of organic carbon in the soil (SOC) as an Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC output(CO2emission = SOC Change x 3.667). The direct and indirect N2O soil emission calculationwas done by multiplying and addingdifferent Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC output parameters with conversion factors according to Schmid et al. [35] and Khalil et al. [36].
Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC did not include parameters for three energy crops considered in the Scenarios. Therefore, we adapted and extended existing crop parameter sets. The short rotation forestry plantation was simulated in Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC with the already implemented poplar. For miscanthus an extra dataset was provided by Schmid [personal notification in 2008]. Red clover and red fescue represented clover-grass mixture. In addition, fertilizer application rates resulting from EFEM were used as input data for the Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC model. To avoid misleading calculations and interpretations crop rotation was considered. Finally, weighted according to the spatial extent of the LUSACs, the output parameters assigned to the LUSACs were summed up.
2.5. Evaluation of effects on target species habitat
The result of EFEM consistsin alist of crop cultivation area for different crops and for each agri-ecological region. So, as landscape related ecological models need land-use patterns as a spatially explicit input, a disaggregationprocedure was applied which assigns to each of 1ha-gridcells covering the study area a specific crop. The method applied per cropfollows two steps: (1) evaluation of agricultural land in regard to its soil suitability/priority according to UMBW [37] and site requirements of relevant crops [38,39] implemented in SLISYS and considering slope, coarse fragment, soil depth, texture, average annual temperature, average annual precipitation and sea level.(2) selection of as much land as indicated by the result of EFEM. The procedure starts allocating the crop with the highest gross margin followed successively by the other crops according to their gross margin. The advantage of the applied procedure, compared to crop share downscaling approaches suggested by Britz and Leip [40], Chakir [41]and Henseler et al. [12], leads to an explicit occupation of a 1-ha-rastercell by a unique crop. The procedure was implemented as an ESRI ArcGIS™ geo-processing model and successfully applied before in a watershed management project [42,43].
The impacts of scenario land-use patterns concerning species habitat performance were then analyzed in GIS-overlaying the crop type distribution asgenerated by the disaggregation and allocation step described above and existing areas of occurrence for target species from [44,45,46]. So an area summary statistics of crop types inside the target species areas was produced. The crop types were classified by an expert-based impact evaluation as documented in Table 2. In a next step, this evaluation scheme led to an area summary statistics for selected target species areas, which was calculated for each of the assessment levels in Table 2. The different scenarios then were compared with regard to their implications of an improvement or a decline of habitat quality. Following the idea of target species as a key species for monitoring species diversity, the different scenarios can be described by this method as more or as less biodiversity friendly.
Table 2. Influence of different crops on habitat quality for Sky Lark (Alaudaarvensis).
| Crop | Assessment |
| Wheat, spring barley, oat, | Very beneficial (++) |
Winter wheat, winter barley, winter rye, winter rapeseed, sugar beet,
potatoes, intertillage | Beneficial (+) |
| Corn, sun flowers | Neutral (O) |
| Maize, clover grass, miscanthus | Adverse (-) |
| Short rotation woods | Very adverse (--) |
Table S1 in supplementary material indicates the habitat quality of land according to different intensification levels considering the change in grassland use according to [47]. Here it is not possible to formulate reasonable rules for a disaggregation as we did for crop cultivation. In the case of the cultivation of grassland we only consider the area of the grassland of a specific type respectively the area of land covered by the assigned evaluation class for the AERs. It is to be mentioned, that this only indicates the decline of the considered land of a specific habitat quality but not of actually occupied habitat area.
2.6. Implementation of nature conservation restrictions
To answer the question of conflicts between energy production and nature conservation we assumed, that a proactive policy follows the strategy of introducing measures targeting nature conservation and protection of aquatic habitat to achieve higher environmental standards in agriculture. So we formulated restrictions in regard to available land for agriculture and intensification. A list of measures you can find in TableS3 in supplementary material. To prepare the scenario calculations three levels of implementation intensity were defined by an estimate of the overall percentage of agricultural land dedicated to the measures. The estimate included complex GIS analyses and the intensively useddatabase of the state level agri-environmental program called "MEKA" [47].The amount of area being funded by the MEKA program in the year 2000 was fixed as "actual standard" level
Level "legal minimum standard" assumes a more rigorous farm strategywhich means that mandatory conservation measures in legally binding conservation areas are the only restrictions assumed for the farmers. As appropriate areas are assumed to be: (a) those sites that are legally regulated by limitations for the intensity of agricultural production (mainly grasslands protected by law for reasons of nature conservation or ground water protection), (b) grasslands on dry soils which have to be cut once per year and which grow up without being fertilized and (c) grasslandson humid soils which have to be cut twice per year and fertilized only up to a maximum of 40 kg N ha−1a−1 (TableS3).
To delineate the area restricted by "improved nature conservation" conservation measures were considered as laid down in the "Action Plan for the Environment 2007-2012" of Baden-Württemberg. The target of those measures consists in a considerable reduction of the loss of species and habitats, corresponding to national and EU targets for the protection of biodiversity. Target species for arable land and grasslands were selected from the State's governmental "Target Species Concept" [45,46] (see TableS2) following the multi-species approach of Lambeck [48]. Then the re-establishment area for the selected target species was estimated by the following steps:
1. Population size was assumed at an approximate level as stated for the 1980s.
2. For birds, typical population densities on farmland enhanced by conservation measures were assumed as an expert attuned mean value derived from literature analysis [49].
3. Using a Geographical Information System (GIS), arable land or grassland area potentially suitable for each species was extracted from GIS land-use layers by eliminating species-specifically disturbed buffer-zones around built-up area, roads and forests. This setting was overlaid by the current spots of occurrence of the species to identify the currently populated area (data was provided by the State Agency for the Environment, Measurements and Nature Conservation of Baden-Württemberg).
4. To demarcate the additional area necessary to support the population size assumed for the 1980s, the largest suitable and coherent area within a 2-km buffer-zone around the currently populated area was taken and added. This step was repeated until the desired area was reached. This approach follows the idea that the development of new habitat is most promising when starting from the largest remaining populations.
5. In addition, areas with a ban on short rotation forestry and miscanthus plantations were introduced. This is due to the fact that breeding birds of open farmland like sky lark, corn bunting or lapwing tend to avoid vegetation structures of several meters of height like woods, groves or higher hedges. This step anticipates that landscape planning needs to exclude short rotation forestry and miscanthus plantations from the territories of these birds.
The area according to the three levels of measures (Table S3) were handed over to EFEM and treated there as being restricted for crop and grassland production. As data input for EFEM, the area of applied conservation and protection measures was set up for each of these levels and for the territory of the whole State of Baden-Württemberg and was then aggregated by the agri-ecological regions.
2.7. Scenarios
The target of the scenario analyses using IMA is to quantify trade-offs and synergies between the expansion of area for the cultivation of energy crops and the target to protect ecosystem integrity and services. Thus scenarios are defined that compare a specified business-as-usual situation with scenarios assuming (a) an extended production of energy crops and (b) an extension of restrictions on agricultural production to support nature conservation. To evaluate the scenarios and applying the IMA a wide range ofeconomic and ecological aspects are considered: gross margin, crop shares, energy supplygreenhouse gas emissions from agricultural and bioenergy production, conflicts concerning habitat of endangered species, and soil erosion, nitrate leaching and nutrient loss.
The scheme of analyzed scenarios is documented in Table 3. We first defined an empirical baseline (BL) for all necessary key parameters. Based on this EFEM model was validated and calibrated (BLMod). Next a business-as-usual (BAU) scenario targeting at the year 2015 was defined considering all scheduled measures of the EU Common Agricultural Policy as well as projections of prices and crop yields. Our study then compares the fixed BAU situation with two types of scenarios:
Table 3. Overview on scenarios and basic assumptions used; for abbreviations see text
| References | Scenarios |
| BL | BLMod | BAU/BAU_Nat | BioE1/BioE1_Nat | BioE2/BioE2_Nat |
| Data type | Statistical | Modelled | Modelled | Modelled | Modelled |
Share of perennial
energy crops on
arable land | No
perennial
energy
crops | No
perennial
energy
crops | No
perennial
energy
crops | No perennial
energy crops | Cultivation on
max. 30% of
suitable arable
land |
Share of annual
energy crops on
land use area | unknown | Max. 4.3%
of crop
rotation | Max. 5% of crop
rotation | No restriction | No restriction |
Max. Share of
cereals in crop
rotation | 57% | 75% | 75% | 75% | 75% |
Max. Share of
winter rape in crop
rotation | 8% | 13% | 18% | 25% | 25% |
Max. Share of
maize silage in
crop rotation | 9% | 50% | 70% | 50-70% | 50-70% |
Level of nature
conservation | Not relevant | Not relevant | Actual
standard/Improved
nature
conservation | Legal minimum
standard/Improved
nature
conservation | Legal minimum
standard/Improved
nature
conservation |
1. Unfixed option for enlargement of agricultural bioenergy crop production without (BioE1) and including perennial crops (BioE2) (specifications see Table 3)
2. Enlargement of nature conservation measures: dedication of new conservation areas, additional subsidies, incentives, compensation measures and areas (see Table 3) and generate "nature friendly" scenarios BAU_Nat, BioE1_Nat, BioE2_Nat.
3. Results
We first report on the economic and environmental impacts of the scenario assumptions of an increased crop cultivation for bioenergy production (3.1). Subsequently and respecting the results of this first analysis the described area restrictions on agricultural production targeting improved nature, soil and water protection are assumed to be introduced and related to income effects (3.2).
3.1. Impacts of an increased cultivation of crops for bioenergy
3.1.1. Effects on agricultural and bioenergy production (EFEM results)
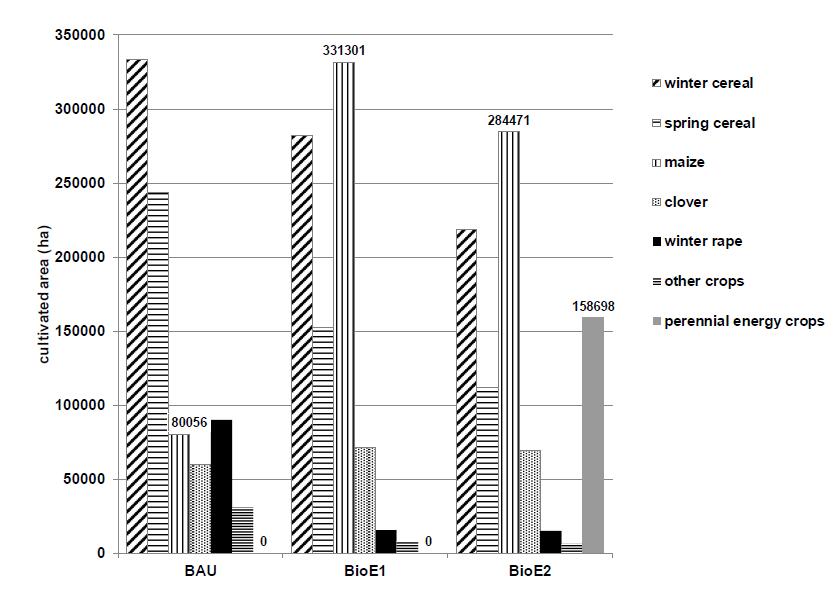
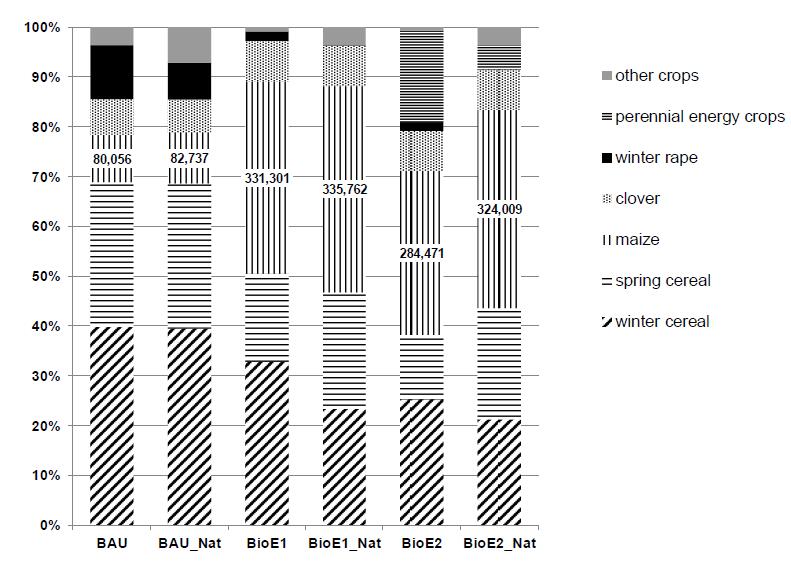
Under the given assumptions of the model the cultivation of energy crops is significantly expanded. Thereby, the cultivation of grain in Baden-Württemberg decreased considerable in both bioenergy scenarios compared to the business as usual scenario (BAU, Figure 4). The straw of the cereals is almost completely combusted. Therefore, the humus balance is obtained by cultivation of catch crops. The option to expand energy crop cultivation led to a large expansion of maize area. In BioE1 maize would account for 40% of arable land. A large proportion of cultivated maize was used for energy production in biogas plants; in some regions more than 90%. In BioE2 perennial energy crops, particularly miscanthus that is economically preferred, grown on 18% of the arable land. Wobei jedoch die ökonomische Vorteilhaftigkeit dieser Kulturen regional sehr unterschiedlich ist. Thus, the proportion of field cropping regions increases to 30% of arable land, in forage growing regions, however, to only slightly more than 1%.Overall, the bioenergy scenarios rarely changed the animal husbandry.
Through conversion of the cultivated energy crops and use of agricultural residues in BioE1 74,200 TJ and in Bio2 86,800 TJ net energyis produced. This would cover 5.3 or 6.2% of final energy demand and is nearly 60% of the present part of renewable energy sources in Baden-Württemberg [49].
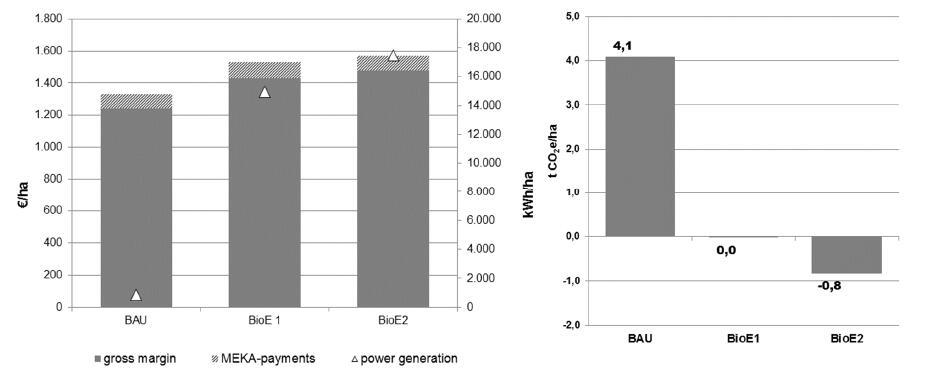
The bio energy scenarios lead to an increase in agricultural gross margins, namely by 15% in BioE1 and by 18% in BioE2 (see Figure 5). In both bioenergy scenarios, equal or more emissions areavoided downstream by bioenergy production than caused by agricultural production. This results in a compensated or negative greenhouse gas balance where the net substitution effect was higher than agricultural emissions. The most savings were reached due to cultivation of perennials crops (BioE2). As the analysis is based on extrapolation of farm gross margins, all bioenergy scenarios would lead to mitigation benefits on farm level. A detailed evaluation of potential mitigation costs, as a result of increased energy crop cultivation, would require a macroeconomic analysis including subsidies, taxes and market effects and is not possible with the IMA presented here.
The effects of the scenarios highly depend on region and farm conditions. Table 4 shows these different reactions on the basis of key parameters for one appropriate farm type model in selected regions. The cultivation structure of almost all farm types showed a clear trend from food production to energy crop production. Energy crops replaced especially the production of winter wheat. Particularly noticeable was the expansion of maize by the factor of seven in intensive livestock farms. While in field cropping and intensive livestock farms maize was almost entirely used for the fermentation in biogas plants, it was mainly fed in forage growing farms. The opportunity to produce bioenergy led to an intensification of grassland particularly for forage-growing farms where a considerable part of the grassland now is used for bioenergy production. For farms with a high percentage of arable land, the cultivation of perennial bioenergy plants, especially miscanthus, was an economically attractive alternative and was often extended up to model constraints.
Table 4. Results for the different farm types in selected AER
| | Field cropping farm (AER 1:
"UnterlandGäue") | Mixed crops-livestock farm (AER 2:
"Rhein/Bodensee") |
| | BAU | BioE1 | BioE2 | BAU | BioE1 | BioE2 |
| Gross margin | €/ha | 546 | 755 | 872 | 811 | 1057 | 1142 |
Power
generation | kWh/ha | 1312 | 29,275 | 22,043 | 1065 | 23,034 | 18,328 |
| Total balance | t CO2e/ha | 2.7 | −3.8 | −6.4 | 2.9 | −2.7 | −4.1 |
| | Forage growing farm(AER 5:
"Allgäu") | Intensive livestock farm (AER 8:
"Bauland/Hohenlohe") |
| | BAU | BioE1 | BioE2 | BAU | BioE1 | BioE2 |
| Gross margin | €/ha | 2256 | 2334 | 2334 | 4566 | 4898 | 4934 |
Power
generation | kWh/ha | 165 | 3666 | 3666 | 1533 | 30,998 | 28,475 |
| Total balance | t CO2e/ha | 7.8 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 5.7 | −2.8 | −3.9 |
Because of a high flexibility in cultivation, especially field cropping farms profited from the option of cultivating energy crops. This can also be shown by the gross margins. While the high gross margins of the forage growing and intensive livestock farms were subject to only small fluctuations, those of field cropping and mixed crops-livestock farms showed a clear increase by 25-60%. The highest energy production was gained by field cropping farms, especially when the cultivation of perennial energy crops was possible (BioE2). The energy production of these farms was about twenty times higher than that of forage growing farms. The forage farm model is least affected by the bioenergy scenarios, because farmland is needed for dairy cows feeding. In contrast, the intensive livestock farm can compensate bioenergy crop cultivation by purchasing feed. The highest savings of emissions are gained in field cropping farms if the cultivation of perennials is possible.
3.1.2. Effects on soil and water
LUSAC-units serve as indicator units being characterized by a broad range of abiotic parameters. Before we discuss the effects of energy crop intensification on soil and water parameters as indicated by Table 6 it is important to state that inherent to scenarios BioE1 and BioE2 (a) there is an increase in total cropping area due to conversion of grassland to arable land and (b) there is a decline in crop and land unit diversity (Table 5). Both land use change effects aredetrimental to soil and water quality.
Table 5. Number of LUSACs, crop diversity and total cropping area in Scenarios BioE1 and BioE2 compared to BL
| Scenario | Number of different LUSACs | Number of different crops | Total cropping area in ha |
| BL | 8767 | 13 | 837,300 |
| BioE1 | 4818 | 9 | 859,700 |
| BioE2 | 5850 | 11 | 863,700 |
Table 6. Balance and alterations of soil and water parameters in Scenarios BioE1 and BioE2 compared
to BL.
| Indicator | Units | Balance | Change compared to BL |
| | BL | BioE1 | BioE2 |
| Water erosion | Gga−1 in BW | 1606 | +228 | −9 |
| kgha−1 a−1 | 1920 | +220 | −70 |
| Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) | Gg a−1in BW | 01 | −679 | −376 |
| kg ha−1 a−1 | 01 | −787 | −434 |
| Nitrous oxide-N | Gg a−1in BW | 4338 | +1890 | +1623 |
| kg ha−1 a−1 | 5.2 | +2.1 | +1.7 |
| Nitrate-N | Gg a−1in BW | 19,889 | +7422 | +5968 |
| kg ha−1 a−1 | 24 | +8.0 | +6.2 |
| 1 If plant production is not changed, an equalised soil-C-balance is assumed at least in the medium term. |
Soil erosion by water, an indicator for the need of soil conservation, summed up for the whole investigation area increased in the scenario BioE1 in comparison to BL (see Table 4) due to increase in monoculture silage maize production for energy use. On the other hand, soil erosion slightly decreased in the scenario BioE2 due to increase in perennial crops. Overall, the soil erosion was on a low level on average, but on sites susceptible to erosion, rates of over 50 Mgha−1a−1 were indicated. The differences were more obvious in scenario BioE1 without perennial energy crops compared to scenario BioE2, which includes cultivation of perennial energy crops. By relating the erosion rate to the LUSAC-area per hectare, a very slight decrease can be stated in BioE2 in the average of all LUSACs, mainly because perennial energy crops covered the soil throughout the year. The model simulations, carried out separately for the eight agri-ecological regions, showed regional differences. The reason was the diverse development of cultivation areas of monocultures, e.g. changes in the proportion of summer crops.
Nitrate leaching as an indicator for the need of groundwater protection increased in the bioenergy scenarios in comparison to BL. This increase was observed regarding the sum over the whole study area as well as relating the rates to LUSAC-area per hectare (see Table 4). Losses in nitrate were higher in scenario BioE1 than in scenario BioE2. This trend is parallel to the proportion of silage maize and perennial energy cropping. The higher amount of nitrogen fertilizer of up to 200 kg Nha−1a−1 on maize assumed in both bioenergy scenarios caused the increase in nitrate leaching. This nitrogen fertilizer originated partly from digestate. The partial substitution of maize for extensively fertilized miscanthus (on average 60 kg Nha−1a−1) and unfertilized short rotation forestry plantations resulted in a lower increase of nitrate leaching in scenario BioE2. However, a leaching of 30 kg Nha−1a−1 from soils with representative site conditions in South West Germany could reach the EU threshold for drinking water, which is at 50 mg nitrate/L [50].
Soil-borne CO2 and N2O emissions as an indicator for the relevance to climate protection concerns were also calculated with Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC using the changes in soil organic carbon (SOC) and the changes in selected parameters of the nitrogen budget. According to this, the annual decrease in SOC stocks, associated with decreasing soil fertility and increasing CO2 emissions, was higher in BioE1 with annual energy crops, compared to the initial stocks in 2003 than in BioE2 with perennial energy crops. This is comparable with the rates of change, summed up over the whole study area as well as for the annual changes related to LUSAC-area per hectare. A plausible reason is the conversion of grassland into arable land leading to SOC losses. Another reason could be the increase of silage maize cropping that led to lower amounts of harvest residues and thus lower carbon accumulation in the topsoil. The development of the N2O emissions showed similar characteristics. The increase of nitrogen fertilizer application (see annotation on nitrate leaching) resulted also in higher N2O emissions. Perennial energy crop cultivation such as miscanthus and short rotation forestry led to lower changes in SOC stocks and in N2O emissions in scenario BioE2, because they do not affect the soil and thus prevent SOC degradation. Therefore, there are less soil-borne CO2 emissions which, together with the omitted application of nitrogen fertilizer, led to the prevention of soil-borne N2O emissions.
3.1.3. Effects on target species
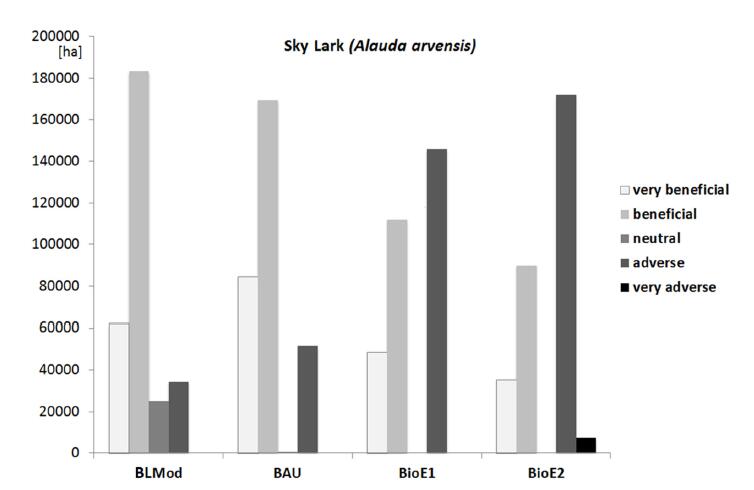
Figure 6 shows the area per habitat impact class as fixed in Table 5 for the sky lark. Crop cover with the attributes "very beneficial" or "beneficial" for habitat suitability declined in the scenario BioE1 and more in BioE2 compared to the BAU scenario. This indicates the effects of the reduction in winter wheat production andon a minor extent also in winter rapeseed, sugar beet and potato production. The area covered with "adverse" or "very adverse" crops clearly increased because of a three- to four-fold expansion in maize production in the bioenergy scenarios and, additionally in BioE2, short rotational forestry and miscanthus production, which are classified as "very adverse".
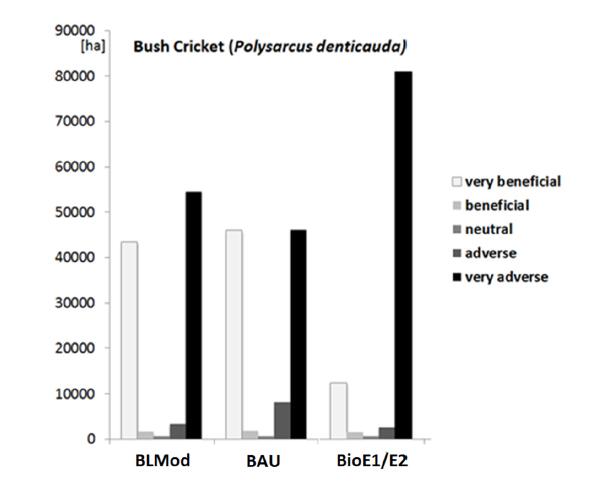
As an example for an impact analysis considering the use of grassland, Figure 7 shows the differences in the area per habitat suitability/impact class as fixed in Table 5 for the bush cricket (Polysarcusdenticauda) in the agri-ecological region "Schwäbische Alb/Baar". This hilly area, with a high portion of extensive use of grasslands, is the most important of only two relicts of occurrence of the Bush Cricket in Germany. Although the aggregate analysis considered the whole agri-ecological region, the sharp decline in extensive production in the bioenergy scenarios causes a risk for further loss of populations of this highly threatened species.
We also analysed in more detail the conflicts between breeding birds of open farmlands and the high-growing miscanthus and short rotation forestry plantations. In scenario BioE2 and as a result of the spatial disaggregation described in chapter 2.5 the area of short rotation forestry plantations covered2,5% of the arable land in the State territory, whereof about 60% was located inside zones that are considered as a conflicting area. On the other hand, simulated spatial distribution ofmiscanthus cultivation in BioE2 covered 14% of the arable land in the State territory, whereof only 14% (17,900 ha) was located inside of ecologically disfavoured zones.
3.2. Impacts of improved nature conservation standards
The following results intend to demonstrate the effects of enlargement of nature conservation measures by dedication of new conservation areas, additional subsidies and compensation measures (see TablesS1 and S2 in supplementary material) on selected EFEM results. In doing so, the previously examined model scenarios are compared to the corresponding "nature friendly" scenarios BAU_Nat, BioE1_Nat, BioE2_Nat.
In most of the regions, improved nature conservation policies led to intensification of the remaining grassland and of the arable land, which were not part of these measures. The strong influence of nature conservation measures on grassland management results in two adjustment measures of the farm models in order to meet the feeding needs for cattle.On the one hand, the cutting frequency and the degree of fertilizing intensity will be considerably increased on the remaining grassland and on the other hand, cultivation of silage maize will be increased Latter is particularly evident at BioE2_Nat where the cultivation of maize silage increases another 14% in comparison to BioE2 (see Figure 8). In grainfarming it becomes evident that in BioE1_Nat and BioE2_Nat spring grain becomes more attractive than winter grain. Furthermore, the cultivation of winter cereals is falling sharply.For example, the winter cereal area in BioE1_nat decline by around 91,500 ha, a drop of 33%.This adjustment was caused due to nature conservation measures, e.g.: Sky lark plots, which have more severe effects on the growth of winter cereals. This illustrates the competition among the requirements for nature conservation and intensive production of bioenergy, feed or food. Spare winter cereal areawas cultivated with summer corn and silo maize.
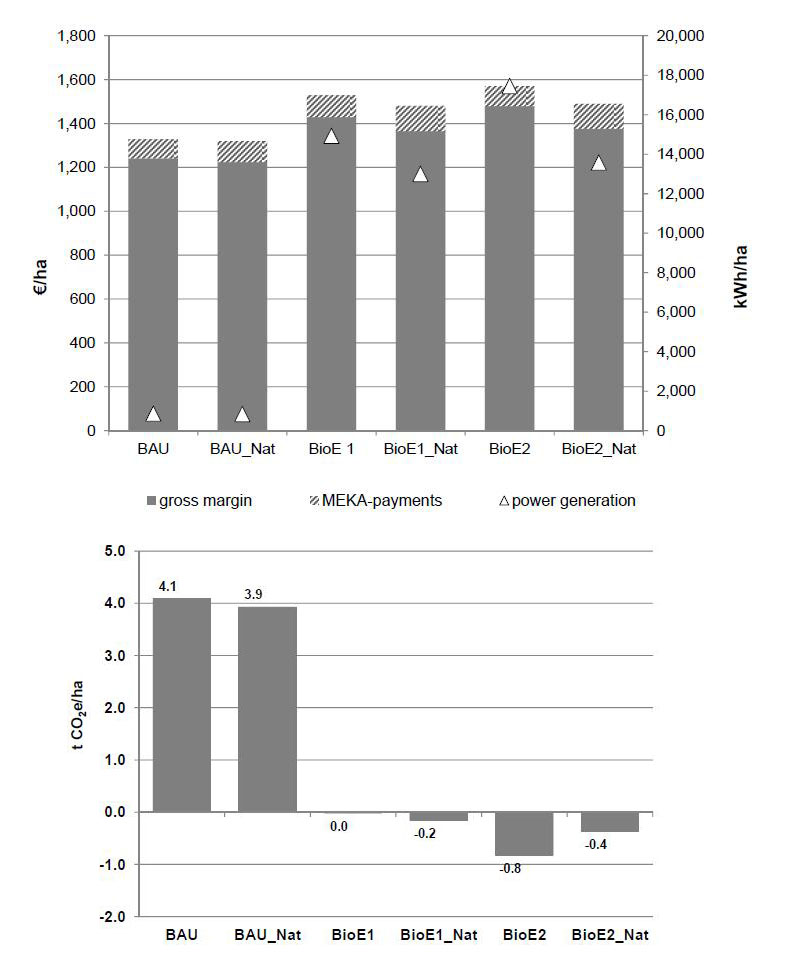
Despite the severe impact of implemented nature conservation measures relative to the utilized agricultural areas, the gross margin decrease is relatively small. The highest decrease amounts to 5% at BioE2 versus BioE2_Nat.
This is based on the fact that most measures can be enhanced by agri-environmental schemes. However, this would entail an increase in MEKA expenditure in Baden-Württemberg. The highest increase would amount to 27% again at BioE2 versus BioE2_Nat. The power generation per hectare utilised agricultural area will decrease by 13% in BioE1_Nat and by 22% in BioE2_Nat. Conservation measures in the BAU scenario will result in a slight reduction of greenhouse gas emissions due to induced extensification effects. In contrast, they decrease the sink effects of greenhouse gas emissions in bioenergy scenarios by a reduced substitute amount of fossil energy sources.
4. Discussion
4.1. Agro-economic results
A central result of the agro-economic modelling with EFEM is the estimated future increase in arable land used for energy crop production. The model calculations show an increase in agricultural gross margin in Baden-Württemberg by up to 18%. Arable farmer would benefit more from this development than forage growing farmer.
However, the simulated cultivation area for energy crops might be overestimated, because the agro-economic model EFEM is a statistically linear programming model that deals with exogenously determined prices. Such a strong limitation of the food and feed production, as the modelling results show, would in reality lead to changes in price of these products. As these price interdependencies could not be represented within the modelling approach, sensitivity analyses with different price assumptions were carried out. They showed that the modelling results were very stable regarding the scale of cultivation of bioenergy resources, especially for the cultivation of perennial energy crops. An alternative option to better show the correlation between farm decisions and market effects is coupling farm based models like EFEM with a partial equilibrium for the agricultural sector [51,52].
From a business point of view the high relative excellence of perennial crops in our analysis is also due to the assumed costs e.g. for fertilizer, pesticides and energy in our model scenarios. Thus, energy crops with low input demand like short rotation forestry or miscanthus would become more competitive. However, in reality, factors such as the comparable high costs of investment for planting and the farmers' attitude towards entrepreneurial risk play an important role for farmers when considering long-term fixing of land-use. These factors were not incorporated in this analytical approach. Model approaches, e.g. Real Options Approaches, can better explain the reluctance for planting observed in reality by taking into consideration complex planning approaches [53,54].
Scenario calculations by EFEM are based on a completely elastic demand, i.e., it is assumed that cultivation of bioenergy crops simultaneouslyallows generate the setup of biogas or combustion for crop conversion. Subsequently, the results represent an economic production potential on farm level.In order to be able to make further statements regarding a realistic demand for agricultural energy crops, EFEM could be coupled with energy market models as TIMES PanEU [55].
Modelling results showed only small reductions in income caused by the implementation of nature conservation measures in the different scenarios. In reality a higher reduction in income would be expected, because the adaptability of farm models was overestimated with this optimized approach. Furthermore no limitation of the payments by agri-environment schemes was assumed. Possible governmental transfer payments for incentives as well as potential costs for monitoring of the nature conservation services need to be added.
By balancing the greenhouse gases, EFEM as a farm based model accounts the emissions from the upstream processes for means of production, agricultural production itself and downstream processes for bioenergy supply. Hereby the greenhouse gas balance in Figure 6 includes also emissions that have been caused by an increase in the purchase of additional feeding stuff as a result of the strong competition in area. A reduction in the degree of self-sufficiency by using food crops for energy production and extending the cultivation of energy crops has not been considered in the EFEM so far. Increased imports of food items would lead to a shift in greenhouse gas emissions into other regions or countries.
4.2. Impacts on soil and water
The scenario results from the EFEM model for maize production area, conversion of grassland and amount of applied fertilizer served as input data for subsequent calculations with the Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC model. The change in soil and water parameters was described applying the principle of sustainability assessment of agriculture with key indicators [56,57,58], e.g. soil erosion for soil conservation, nitrate leaching for water protection or soil-borne greenhouse gas emissions for climate change mitigation [59,60]. With regard to such indicators, the plausibility of the Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC modelling results is satisfying in comparison to single and representative surveys. The modelled mean values of C content are comparable to several surveys on increases and decreases of land use changes [61,62,63]. The modelled nitrogen losses by nitrate leaching is still in the frame derived from the results of governmental controlling campaigns in southwestern Germany [64]. The nitrous oxide emissions that have been estimated by using factors cited by Schmid [36] ranged in the frame as reviewed by Kaiser [65] on soils in Germany. The modelled erosion is equal to merely about 20% of the mass observed in south west Germany and Bavaria [66,67].
The changes in the investigated parameters indicating resource conservation are less distinct when integrating perennial energy crops such as short rotation forestry plantations or miscanthus into the cropping system (refer to Table 6). However, not included in the considerations are additional conservation measures like reduced soil tillage that offer the possibility for compensation [4]. Model results from Ehttps://www.aimspress.com/aimspress-data/aimsagri/2017/1/PIC (refer to Table 6) showed that adverse environmental effects increased if energy crop production increased, mainly because of grassland conversion to crop land. Annual energy crops such as silage maize (scenario BioE1) caused higher adverse ecological impacts than perennial energy crops like short rotation forestry or miscanthus (scenario BioE2). In the modelled area, positive effects of perennial energy crop production compensated negative effects of grassland conversion to crop land and annual energy crop production (see scenario BioE2 in Table 6).
4.3. Species habitat effects
From the results we have to state a clear decrease in habitat potentials for the selected target species and the contribution to biodiversity they represent when energy crop share increases (Figures 6 and 7). Main factors are the drastic increase in maize cultivation, the intensification of grassland use and grassland conversion to crop land. These findings have been expected, but we have shown that nature conservation regulations can prevent such effects without severe economic effects (Figure 9). Everaars et al. [6] report from modelling experiments and state considering an intensive bioenergy scenario, "that the decrease in breeding pair density … could be fully mitigated for all the considered bird species through 10% set-aside". But they also state that, if there is an increase of dominance or a spatial agglomeration of a single energy crop (e.g., maize), mitigation is very difficult. The first findings confirm our result that nature conservation is not really a kick out argument for cost effective energy crop agriculture, and the second statement meets our findings for BioE2, where maize is the dominating crop and severely affects sky lark habitat quality.
As stated in 3.2 the bioenergy scenarios without applying "improved nature conservation", grasslands are massively converted to arable land until the Baden-Württemberg specific legal limit for grassland conversion is reached. Especially in cases of low intensity grassland, a dramatic loss of biodiversity and negative effects concerning soil ecosystem services is to be expected. These processes are well known and were approved by this study. The second question was whether trade-offs are occurring if the requirements for "improved nature conservation" are applied. The study shows that even under "improved nature conservation" restrictions, bioenergy crop production can increase considerably (refer to Figure 9 and compare in the left chart columns 4 and 6 with column 2), while the greenhouse gas balance for the agricultural sector is nearly equalized (Figure 9 right chart, columns 4 and 6). In this case, the funding of conservation measures underagri-environmental programs needs to be flexibly increased to keep up with rising income effects from energy crop cultivation. In addition, a planned regionalization of specific conservation measures based on the distribution of indicator species would highly improve their efficiency.Our study depicts rather positive effects of perennial energy crops on agricultural land. Aversion of farmers to long-term fixation of land use could be reduced by planting premiums, but for this aspect more research is needed.
5. Conclusion
Our approach indicatesuncovered effects, conflicts and synergies between agriculture and ecology. It suggests a successful method to consider trade-off scenarios which are able to support policy making. The results show that a coexistence of energy use driven intensification and nature conservation is not a utopian promise. It is just a question of control considering where (locations in respect to soil conditions) and what (share of crops and short rotation trees). And politicians must not fear to demand that this is done rigorously with due respect. Farmers income must not come under pressure and this is a good basis to convince them that it is their own benefit if ecosystem services like pollination are secured by the integrity of the ecosystem as a whole.
Acknowledgments
This article includes results which are fundamental to the doctoral theses of Dr. Heike Weippertand Dr. Angelika Konold. The research reported in this article was funded by the environmental research fund of the German State of Baden-Württemberg BWPLUS (project IDs BWB27003, BWB27006, BWK27003). We are grateful to Erwin Schmid (University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna, Austria) for providing a data set with crop parameters formiscanthus. Many thanks to Susanne Wagner for proof-reading and fruitful discussions.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: