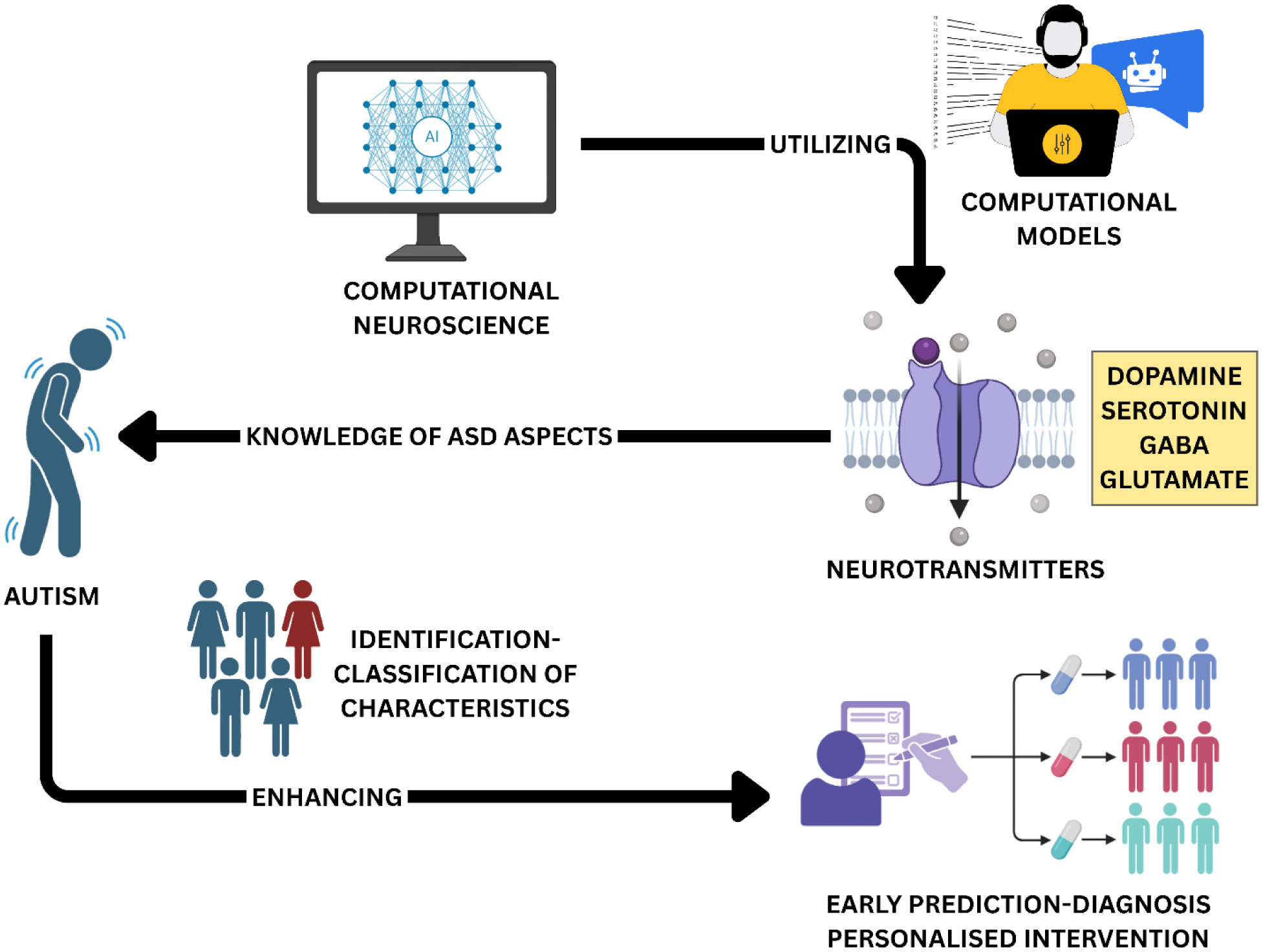
Computational modeling of excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) balance offers transformative insights into the neurobiological underpinnings of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In this review, we examined the integration of neurotransmitter dynamics and genetic factors into multiscale computational frameworks to elucidate the mechanisms driving E/I dysregulation in ASD. We explored the pivotal roles of glutamate and GABA, the primary excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters, and the modulatory impact of serotonin and dopamine (DA), in shaping neural circuit stability, behavioral outcomes, and ASD core symptoms. Genetic mutations affecting synaptic proteins such as SHANK3, GRIN2A, and GABRB3 were highlighted for their capacity to disturb synaptic scaffolding and glutamatergic and GABAergic signaling, thereby shifting the E/I ratio. Computational approaches, ranging from detailed neuronal simulations to neural mass and spiking network models, captured the heterogeneous manifestations of E/I imbalance and aligned with molecular, neuroimaging, and electrophysiological findings in ASD. We discussed how these models informed individualized diagnostic strategies, enabled prediction of treatment responses, and offered targets for precision medicine. Major challenges included methodological inconsistencies, neurochemical measurement discrepancies, polygenic interactions, and the translation of model predictions into clinical practice. We concluded that the integration of neurotransmitter and genetic data within advanced computational models represents a significant advance toward unraveling ASD pathophysiology, with the promise of developing dynamic, personalized interventions. Ongoing efforts should emphasize longitudinal data, multiomic integration, sex-specific trajectories, and cross-disciplinary collaboration to further the clinical applicability and translational potential of computational E/I balance modeling in autism research.
Graphical abstract
Citation: Dilip Madia, Mujibullah Sheikh, Anil Pethe, Darshan Telange, Surendra Agrawal. Excitatory/Inhibitory balance in autism spectrum disorders: Integrating genetic, neurotransmitter and computational perspectives[J]. AIMS Neuroscience, 2025, 12(4): 635-675. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2025031
Computational modeling of excitatory/inhibitory (E/I) balance offers transformative insights into the neurobiological underpinnings of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In this review, we examined the integration of neurotransmitter dynamics and genetic factors into multiscale computational frameworks to elucidate the mechanisms driving E/I dysregulation in ASD. We explored the pivotal roles of glutamate and GABA, the primary excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters, and the modulatory impact of serotonin and dopamine (DA), in shaping neural circuit stability, behavioral outcomes, and ASD core symptoms. Genetic mutations affecting synaptic proteins such as SHANK3, GRIN2A, and GABRB3 were highlighted for their capacity to disturb synaptic scaffolding and glutamatergic and GABAergic signaling, thereby shifting the E/I ratio. Computational approaches, ranging from detailed neuronal simulations to neural mass and spiking network models, captured the heterogeneous manifestations of E/I imbalance and aligned with molecular, neuroimaging, and electrophysiological findings in ASD. We discussed how these models informed individualized diagnostic strategies, enabled prediction of treatment responses, and offered targets for precision medicine. Major challenges included methodological inconsistencies, neurochemical measurement discrepancies, polygenic interactions, and the translation of model predictions into clinical practice. We concluded that the integration of neurotransmitter and genetic data within advanced computational models represents a significant advance toward unraveling ASD pathophysiology, with the promise of developing dynamic, personalized interventions. Ongoing efforts should emphasize longitudinal data, multiomic integration, sex-specific trajectories, and cross-disciplinary collaboration to further the clinical applicability and translational potential of computational E/I balance modeling in autism research.

Graphical abstract

| [1] |
Sohn JS, Lee E, Kim JJ, et al. (2025) Implementation of generative AI for the assessment and treatment of autism spectrum disorders: a scoping review. Front Psychiatry 16: 1628216. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1628216 
|
| [2] |
Wilson RB, Thompson AR, Rowse G, et al. (2023) The experience of seeking, receiving, and reflecting upon a diagnosis of autism in the UK: A meta-synthesis of qualitative studies conducted with autistic individuals. Res Autism Spectr Disord 103: 102135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2023.102135 
|
| [3] |
Wang J, Fu K, Chen L, et al. (2017) Increased Gray Matter Volume and Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Somatosensory Cortex and their Relationship with Autistic Symptoms in Young Boys with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Physiol 8: 588. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00588 
|
| [4] | Masood K, Kashef R (2022) Integrating Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) for Efficient Diagnosis of Autism. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine . Cham: Springer International Publishing 110-121. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-09342-5_11 |
| [5] | McNeil CB, Quetsch LB, Anderson CM (2018) What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder?. Handbook of Parent-Child Interaction Therapy for Children on the Autism Spectrum . Cham: Springer International Publishing 3-26. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03213-5 |
| [6] | J. Paul TaylorNeuron (2017)95: 999-1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.08.027 |
| [7] |
Beauvois L, Kverno K (2020) Challenges in Treating Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Implications for Psychiatric–Mental Health Nurse Practitioners. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv 58: 7-12. https://doi.org/10.3928/02793695-20201112-02 
|
| [8] | Sadiq S, Noor F (2023) Exploring the Relationship of Mind Skills and Social Skills With Autistic Traits Among Diagnosed Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Pak J Soc Res 5: 597-603. https://doi.org/10.52567/pjsr.v5i01.1382 |
| [9] |
Creswell C, Waite P, Hudson J (2020) Practitioner Review: Anxiety disorders in children and young people – assessment and treatment. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 61: 628-643. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.13186 
|
| [10] |
Moore T, Zirnsak M (2017) Neural Mechanisms of Selective Visual Attention. Annu Rev Psychol 68: 47-72. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033400 
|
| [11] |
Joseph L, Spence S, Thurm A (2013) Autism and Autism Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Overview. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/med/9780199744312.003.0002 
|
| [12] |
Folstein SE (2006) The clinical spectrum of autism. Clin Neurosci Res 6: 113-117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnr.2006.06.008 
|
| [13] |
Dai H, Jiang Y, Liu S, et al. (2024) Dietary flavonoids modulate the gut microbiota: A new perspective on improving autism spectrum disorder through the gut-brain axis. Food Res Int 186: 114404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114404 
|
| [14] | Sidjaja FF (2024) The growing definition of Autism. Int J Disabil Dev Educ 2024: 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1080/1034912x.2024.2393382 |
| [15] |
McKenna K, Prasad S, Cooper J, et al. (2024) Incidence of Otolaryngological Manifestations in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Special Focus on Auditory Disorders. Audiol Res 14: 35-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14010005 
|
| [16] | Changeux JP (1996) Neurotransmitter receptors in the changing brain: allosteric transitions, gene expression and pathology at the molecular level. Cambridge University Press. |
| [17] |
Joseph D, Pidathala S, Mallela AK, et al. (2019) Structure and Gating Dynamics of Na+/Cl– Coupled Neurotransmitter Transporters. Front Mol Biosci 6: 80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2019.00080 
|
| [18] | Opladen T, Cortès-Saladelafont E, Mastrangelo M, et al. (2016) The International Working Group on Neurotransmitter related Disorders (iNTD): A worldwide research project focused on primary and secondary neurotransmitter disorders. Mol Genet Metab Rep 9: 61-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgmr.2016.09.006 |
| [19] |
Calabro FJ, Parr AC, Sydnor VJ, et al. (2025) Leveraging ultra-high field (7T) MRI in psychiatric research. Neuropsychopharmacology 50: 85-102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-024-01980-6 
|
| [20] |
Dankoski EC, Wightman RM (2013) Monitoring serotonin signaling on a subsecond time scale. Front Integr Neurosci 7: 44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2013.00044 
|
| [21] |
Watson CJ, Venton BJ, Kennedy RT (2006) In Vivo Measurements of Neurotransmitters by Microdialysis Sampling. Anal Chem 78: 1391-1399. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0693722 
|
| [22] |
Westerink BHC, Timmerman W (1999) Do neurotransmitters sampled by brain microdialysis reflect functional release?. Anal Chim Acta 379: 263-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-2670(98)00407-3 
|
| [23] |
Ungerstedt U, Hallström Å (1987) In vivo microdialysis - a new approach to the analysis of neurotransmitters in the brain. Life Sci 41: 861-864. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(87)90181-0 
|
| [24] |
Lohani S, Martig AK, Underhill SM, et al. (2018) Burst activation of dopamine neurons produces prolonged post-burst availability of actively released dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 43: 2083-2092. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0088-7 
|
| [25] |
Zhou N, Huo F, Yin C (2024) Advances neurotransmitter fluorescent probe based on chemical reaction or molecular assemble and its neuroimaging. Coord Chem Rev 518: 216062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2024.216062 
|
| [26] |
Lea-Carnall CA, El-Deredy W, Stagg CJ, et al. (2023) A mean-field model of glutamate and GABA synaptic dynamics for functional MRS. Neuroimage 266: 119813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119813 
|
| [27] |
Alambyan V, Pace J, Sukpornchairak P, et al. (2020) Imaging Guidance for Therapeutic Delivery: The Dawn of Neuroenergetics. Neurotherapeutics 17: 522-538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-020-00843-4 
|
| [28] |
Xu XB, Murtada K, Pawliszyn J (2021) Determination of selected volatile terpenes in fish samples via solid phase microextraction arrow coupled with GC-MS. Talanta 221: 121446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121446 
|
| [29] |
Cai Z, Wang Z, Xia Y, et al. (2021) Tailored Catalytic Nanoframes from Metal–Organic Frameworks by Anisotropic Surface Modification and Etching for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 60: 4747-4755. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202010618 
|
| [30] |
Dhailappan A, Samiappan S (2022) Impact of Diet on Neurotransmitters. Role of Nutrients in Neurological Disorders . Singapore: Springer 363-383. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8158-5_20 
|
| [31] |
Celada P, Puig MV, Artigas F (2013) Serotonin modulation of cortical neurons and networks. Front Integr Neurosci 7: 25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2013.00025 
|
| [32] |
Giovanni GD, Matteo VD, Pierucci M, et al. (2006) Central Serotonin2C Receptor: From Physiology to Pathology. Curr Top Med Chem 6: 1909-1925. https://doi.org/10.2174/156802606778522113 
|
| [33] |
Sergeyev V, Hökfelt T, Hurd Y (1999) Serotonin and substance P co-exist in dorsal raphe neurons of the human brain. Neuroreport 10: 3967-3970. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199912160-00044 
|
| [34] |
Kurahashi H, Kunisawa K, Tanaka KF, et al. (2025) Autism spectrum disorder-like behaviors induced by hyper-glutamatergic NMDA receptor signaling through hypo-serotonergic 5-HT1A receptor signaling in the prefrontal cortex in mice exposed to prenatal valproic acid. Neuropsychopharmacology 50: 739-750. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-024-02004-z 
|
| [35] |
Tatti R, Haley MS, Swanson OK, et al. (2017) Neurophysiology and Regulation of the Balance Between Excitation and Inhibition in Neocortical Circuits. Bio Psychiatry 81: 821-831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.09.017 
|
| [36] | Baik JH (2013) Dopamine Signaling in reward-related behaviors. Front Neural Circuits 7: 152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2013.00152 |
| [37] |
Brandenburg C, Soghomonian JJ, Zhang K, et al. (2020) Increased Dopamine Type 2 Gene Expression in the Dorsal Striatum in Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder Suggests Alterations in Indirect Pathway Signaling and Circuitry. Front Cell Neurosci 14: 577858. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.577858 
|
| [38] |
Teixeira MR, Silva T, Felício RDFM, et al. (2025) Exploring the genetic contribution in obesity: An overview of dopaminergic system genes. Behav Brain Res 480: 115401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115401 
|
| [39] |
Mann LG, Claassen DO (2024) Mesial temporal dopamine: From biology to behaviour. Eur J Neurosci 59: 1141-1152. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.16209 
|
| [40] |
Francis P (2007) The Rationale for Glutamatergic Therapy in Alzheimer's Disease. Pharmacological Mechanisms in Alzheimer's Therapeutics . New York: Springer 105-112. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-71522-3_6 
|
| [41] |
Sugiyama H, Ito I, Okada D (1990) Roles of metabotropic and ionotropic glutamate receptors in the long-term potentiation of hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Adv Exp Med Biol 268: 387-394. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5769-8_42 
|
| [42] | Djuričić B (2002) Glutamate in brain: transmitter and poison. Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med 47: 55-76. |
| [43] |
Benarroch E (2021) Glutamatergic Transmission and Synaptopathies. Neuroscience for Clinicians . New York: Oxford Academic 296-316. https://doi.org/10.1093/MED/9780190948894.003.0017 
|
| [44] | Yamamoto C (1992) Glutamic acid as an excitatory neurotransmitter. Nihon Rinsho 50: 1497-1502. |
| [45] |
Yang JL, Sykora P, Wilson D, et al. (2011) The excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate stimulates DNA repair to increase neuronal resiliency. Mech Ageing Dev 132: 405-411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2011.06.005 
|
| [46] |
Andersen JV, Markussen KH, Jakobsen E, et al. (2021) Glutamate metabolism and recycling at the excitatory synapse in health and neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology 196: 108719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108719 
|
| [47] |
Ng K, O'dowd B, Rickard N, et al. (1997) Complex Roles of Glutamate in the Gibbs—Ng Model of One-trial Aversive Learning in the New-born Chick. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21: 45-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7634(95)00079-8 
|
| [48] |
Rahn K, Slusher B, Kaplin A (2012) Glutamate in CNS neurodegeneration and cognition and its regulation by GCPII inhibition. Curr Med Chem 19: 1335-1345. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986712799462649 
|
| [49] |
Maragakis N, Rothstein J (2001) Glutamate transporters in neurologic disease. Arch Neurol 58: 365-370. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHNEUR.58.3.365 
|
| [50] | Chen RJ, Sharma S (2025) GABA Receptor. StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. |
| [51] | Ochoa-de la Paz LD, Gulias-Cañizo R, Ruíz-Leyja ED, et al. (2021) The role of GABA neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system, physiology, and pathophysiology. Rev Mex Neuroci 22: 67-76. https://doi.org/10.24875/rmn.20000050 |
| [52] |
Wang DD, Kriegstein AR, Ben-Ari Y (2008) GABA Regulates Stem Cell Proliferation before Nervous System Formation. Epilepsy Curr 8: 137-139. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1535-7511.2008.00270.x 
|
| [53] |
Alabdali A, Ben Bacha A, Alonazi M, et al. (2025) Comparative evaluation of certain biomarkers emphasizing abnormal GABA inhibitory effect and glutamate excitotoxicity in autism spectrum disorders. Front Psychiatry 16: 1562631. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1562631 
|
| [54] |
Schousboe A, Bak LK, Waagepetersen H (2013) Astrocytic Control of Biosynthesis and Turnover of the Neurotransmitters Glutamate and GABA. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4: 102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2013.00102 
|
| [55] |
Andersen JV, Schousboe A (2023) Milestone Review: Metabolic dynamics of glutamate and GABA mediated neurotransmission-The essential roles of astrocytes. J Neurochem 166: 109-137. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15811 
|
| [56] |
Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen H (2006) The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem 98: 641-653. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03913.x 
|
| [57] |
Hertz L, Rothman D (2016) Glucose, Lactate, β-Hydroxybutyrate, Acetate, GABA, and Succinate as Substrates for Synthesis of Glutamate and GABA in the Glutamine-Glutamate/GABA Cycle. Adv Neurobiol 13: 9-42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45096-4_2 
|
| [58] |
Andersen JV, Schousboe A, Verkhratsky A (2022) Astrocyte energy and neurotransmitter metabolism in Alzheimer's disease: Integration of the glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle. Prog Neurobiol 217: 102331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102331 
|
| [59] |
Schousboe A (2018) Metabolic signaling in the brain and the role of astrocytes in control of glutamate and GABA neurotransmission. Neurosci Lett 689: 11-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.01.038 
|
| [60] |
Uscătescu LC, Hyatt CJ, Dunn J, et al. (2025) Using the excitation/inhibition ratio to optimize the classification of autism and schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry 15: 234. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-025-03455-8 
|
| [61] |
Pretzsch CM, Floris DL (2020) Balancing excitation and inhibition in the autistic brain. eLife 9: e60584. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.60584 
|
| [62] |
Bruining H, Hardstone R, Juarez-Martinez EL, et al. (2020) Measurement of excitation-inhibition ratio in autism spectrum disorder using critical brain dynamics. Sci Rep 10: 9195. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65500-4 
|
| [63] |
Dickinson A, Jones M, Milne E (2016) Measuring neural excitation and inhibition in autism: Different approaches, different findings and different interpretations. Brain Res 1648: 277-289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.07.011 
|
| [64] |
Pietropaolo S, Provenzano G (2022) Editorial: Targeting Excitation-Inhibition Imbalance in Neurodevelopmental and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front Neurosci 16: 968115. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.968115 
|
| [65] |
Duggins P, Eliasmith C (2022) Constructing functional models from biophysically-detailed neurons. PLoS Comput Biol 18: e1010461. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010461 
|
| [66] |
Haufler D, Ito S, Koch C, et al. (2023) Simulations of cortical networks using spatially extended conductance-based neuronal models. J Physiol 601: 3123-3139. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp284030 
|
| [67] |
Koravuna S, Sanaullah S, Jungeblut T, et al. (2024) Spiking Neural Network Models Analysis on Field Programmable Gate Arrays. ICONIC 2024: 259-270. https://doi.org/10.59200/iconic.2024.027 
|
| [68] | Horacio Rotstein, Farzan Nadim (2020) Neurons and Neural Networks: Computational Models. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences . Wiley 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0000089.pub4 |
| [69] |
Carlu M, Chehab O, Dalla Porta L, et al. (2019) A mean-field approach to the dynamics of networks of complex neurons, from nonlinear Integrate-and-Fire to Hodgkin-Huxley models. J Neurophysiol 123: 1042-1051. https://doi.org/10.1101/870345 
|
| [70] |
Rodrigues S, Chizhov AV, Marten F, et al. (2010) Mappings between a macroscopic neural-mass model and a reduced conductance-based model. Biol Cybern 102: 361-371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0372-z 
|
| [71] |
Zeng Y, Zhao D, Zhao F, et al. (2023) BrainCog: A spiking neural network based, brain-inspired cognitive intelligence engine for brain-inspired AI and brain simulation. Patterns (N Y) 4: 100789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2023.100789 
|
| [72] |
Tan H, Van Dijken S (2024) A universal neuromorphic vision processing system. Nat Electron 7: 946-947. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01288-9 
|
| [73] |
Verhellen J, Beshkov K, Amundsen S, et al. (2023) Multitask Learning of Biophysically-Detailed Neuron Models. PLoS Comput Biol 20: e1011728. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.05.570220 
|
| [74] |
Agnes EJ, Vogels TP (2024) Co-dependent excitatory and inhibitory plasticity accounts for quick, stable and long-lasting memories in biological networks. Nat Neurosci 27: 964-974. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-024-01597-4 
|
| [75] |
Zhang Y, Wu J, Zheng Y, et al. (2024) Voltage Gated Ion Channels and Sleep. J Membr Biol 257: 269-280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-024-00325-0 
|
| [76] |
Szi Hui T, Khairi Ishak M, Fauzi Packeer Mohamed M, et al. (2021) Balancing Excitation and Inhibition of Spike Neuron Using Deep Q Network (DQN). J Phys Conf Ser 1755: 012004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1755/1/012004 
|
| [77] |
Gogolla N, LeBlanc JJ, Quast KB, et al. (2009) Common circuit defect of excitatory-inhibitory balance in mouse models of autism. J Neurodevelop Disord 1: 172-181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11689-009-9023-x 
|
| [78] |
Hollestein V, Poelmans G, Forde NJ, et al. (2021) Excitatory/inhibitory imbalance in autism: the role of glutamate and GABA gene-sets in symptoms and cortical brain structure. Transl Psychiatry 13: 18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-023-02317-5 
|
| [79] | Lee SE, Kim JA, Chang S (2018) nArgBP2-SAPAP-SHANK, the core postsynaptic triad associated with psychiatric disorders. Exp Mol Med 50: 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-017-0018-5 |
| [80] |
Ulloa A, Horwitz B (2016) Embedding Task-Based Neural Models into a Connectome-Based Model of the Cerebral Cortex. Front Neuroinform 10: 32. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2016.00032 
|
| [81] |
Lin HC, Gean PW, Wang CC, et al. (2013) The Amygdala Excitatory/Inhibitory Balance in a Valproate-Induced Rat Autism Model. PLoS One 8: e55248. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055248 
|
| [82] |
Davenport EC, Szulc BR, Drew J, et al. (2019) Autism and Schizophrenia-Associated CYFIP1 Regulates the Balance of Synaptic Excitation and Inhibition. Cell Rep 26: 2037-2051.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.092 
|
| [83] |
Baker C, Zhu V, Rosenbaum R (2020) Nonlinear stimulus representations in neural circuits with approximate excitatory-inhibitory balance. PLoS Comput Biol 16: e1008192. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008192 
|
| [84] |
Noel JP, Balzani E, Acerbi L, et al. (2025) A common computational and neural anomaly across mouse models of autism. Nat Neurosci 28: 1519-1532. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-01965-8 
|
| [85] |
Lanillos P, Oliva D, Philippsen A, et al. (2020) A review on neural network models of schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder. Neural Netw 122: 338-363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.10.014 
|
| [86] |
Pourhamzeh M, Moravej FG, Arabi M, et al. (2022) The Roles of Serotonin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42: 1671-1692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01064-9 
|
| [87] |
Cortes-Altamirano JL, Olmos-Hernandez A, Jaime HB, et al. (2018) Review: 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 Receptors and their Role in the Modulation of Pain Response in the Central Nervous System. Curr Neuropharmacol 16: 210-221. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170911121027 
|
| [88] | Carr FB (2013) A molecular and behavioural analysis of descending facilitation in a model of joint inflammation. Doctoral dissertation, UCL . [cited 2025 October 16]. Available from: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1385739 |
| [89] |
Kosillo P, Bateup HS (2021) Dopaminergic Dysregulation in Syndromic Autism Spectrum Disorders: Insights From Genetic Mouse Models. Front Neural Circuits 15: 700968. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2021.700968 
|
| [90] |
Nguyen M, Roth A, Kyzar EJ, et al. (2014) Decoding the contribution of dopaminergic genes and pathways to autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Neurochem Int 66: 15-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.01.002 
|
| [91] |
Santos A, Caramelo F, De Melo JB, et al. (2020) Dopaminergic Gene Dosage in Autism versus Developmental Delay: From Complex Networks to Machine Learning approaches. J Pers Med 12: 1579. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.28.065987 
|
| [92] | Qi C, Chen A, Mao H, et al. (2022) Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Imbalance Caused by Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Deficits During Development in a Valproic Acid Mouse Model of Autism. Front Mol Neurosci 15: 275. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2022.860275 |
| [93] | Wang J, Chai R, Lin J, et al. Dopaminergic signaling is linked to neurodevelopmental deficits in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) (2022). https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1502564/v1 |
| [94] |
Song Q, Wei A, Xu H, et al. (2024) An ACC–VTA–ACC positive-feedback loop mediates the persistence of neuropathic pain and emotional consequences. Nat Neurosci 27: 272-285. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01519-w 
|
| [95] |
El-Ansary A, Al-Ayadhi L (2014) GABAergic/glutamatergic imbalance relative to excessive neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorders. J Neuroinflammation 11: 189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0189-0 
|
| [96] |
Alymov AA, Kapitsa IG, Voronina TA (2021) Neurochemical Mechanisms of Pathogenesis and Pharmacological Correction of Autism Spectrum Disorders: Current Concepts and Prospects. Neurochem J 15: 129-138. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1819712421020033 
|
| [97] |
Lenart J, Augustyniak J, Lazarewicz JW, et al. (2020) Altered expression of glutamatergic and GABAergic genes in the valproic acid-induced rat model of autism: A screening test. Toxicology 440: 152500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2020.152500 
|
| [98] |
Hajri M, Halayem S, Lakhal MH, et al. (2015) Autism Spectrum Disorders: Focus On Neuronal Synapses (literature Review). Eur Psychiatry 30: 572. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-9338(15)31912-X 
|
| [99] |
Tasnim A, Alkislar I, Hakim R, et al. (2024) The developmental timing of spinal touch processing alterations predicts behavioral changes in genetic mouse models of autism spectrum disorders. Nat Neurosci 27: 484-496. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01552-9 
|
| [100] |
Song Y, Hupfeld KE, Davies-Jenkins CW, et al. (2024) Brain glutathione and GABA+ levels in autistic children. Autism Res 17: 512-528. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.3097 
|
| [101] |
Nardi L, Chhabra S, Leukel P, et al. (2023) Neuroanatomical changes of ionotropic glutamatergic and GABAergic receptor densities in male mice modeling idiopathic and syndromic autism spectrum disorder. Front Psychiatry 14: 1199097. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1199097 
|
| [102] |
Tien NW, Kerschensteiner D (2018) Homeostatic plasticity in neural development. Neural Dev 13: 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13064-018-0105-x 
|
| [103] |
Wenner P (2014) Homeostatic synaptic plasticity in developing spinal networks driven by excitatory GABAergic currents. Neuropharmacology 78: 55-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.058 
|
| [104] |
Denaxa M, Neves G, Burrone J, et al. (2018) Homeostatic Regulation of Interneuron Apoptosis During Cortical Development. J Exp Neurosci 12: 1179069518784277. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179069518784277 
|
| [105] |
Andrei AR, Akil AE, Kharas N, et al. (2023) Rapid compensatory plasticity revealed by dynamic correlated activity in monkeys in vivo. Nat Neurosci 26: 1960-1969. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01446-w 
|
| [106] | Sarti F Role of retinoic acid signaling in homeostatic synaptic plasticity, UC Berkeley (2013). [cited 2025 October 16]. Available from: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2st131zg |
| [107] | Papatheodoropoulos C (2025) Compensatory Regulation of Excitation/Inhibition Balance in the Ventral Hippocampus: Insights from Fragile X Syndrome. Biology (Basel) 14: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040363 |
| [108] |
Tang B, Zhao J, Zhang C, et al. (2024) Dysregulation of parvalbumin expression and neurotransmitter imbalance in the auditory cortex of the BTBR mouse model of autism spectrum disorder. Dev Neurobiol 84: 251-263. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.22952 
|
| [109] |
Coradin J, Castro YVCD, Caiado FL, et al. (2025) Unraveling The Complex Genetic Architecture Of Autism Spectrum Disorder: Insights Into Pathophysiology And Therapeutic Implications. REASE 10: 2421-2429. https://doi.org/10.51891/rease.v10i8.15296 
|
| [110] |
Canitano R, Palumbi R (2021) Excitation/Inhibition Modulators in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Current Clinical Research. Front Neurosci 15: 753274. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.753274 
|
| [111] | Naskar A, Vattikonda A, Deco G, et al. (2021) Multiscale dynamic mean field (MDMF) model relates resting-state brain dynamics with local cortical excitatory–inhibitory neurotransmitter homeostasis. Netw Neurosci 5: 757-782. https://doi.org/10.1162/netn_a_00197 |
| [112] |
Maier S, Düppers AL, Runge K, et al. (2022) Increased prefrontal GABA concentrations in adults with autism spectrum disorders. Autism Res 15: 1222-1236. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2740 
|
| [113] |
DeMayo MM, Harris AD, Song YJC, et al. (2021) Age-related parietal GABA alterations in children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res 14: 859-872. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2487 
|
| [114] |
Arons MH, Thynne CJ, Grabrucker AM, et al. (2012) Autism-Associated Mutations in ProSAP2/Shank3 Impair Synaptic Transmission and Neurexin–Neuroligin-Mediated Transsynaptic Signaling. J Neurosci 32: 14966-14978. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2215-12.2012 
|
| [115] |
Monteiro P, Feng G (2017) SHANK proteins: roles at the synapse and in autism spectrum disorder. Nat Rev Neurosci 18: 147-157. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.183 
|
| [116] |
Sala C, Vicidomini C, Bigi I, et al. (2015) Shank synaptic scaffold proteins: keys to understanding the pathogenesis of autism and other synaptic disorders. J Neurochem 135: 849-858. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13232 
|
| [117] |
Yi F, Danko T, Botelho SC, et al. (2016) Autism-associated SHANK3 haploinsufficiency causes Ih channelopathy in human neurons. Science 352: aaf2669. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf2669 
|
| [118] | Lee J, Chung C, Ha S, et al. (2015) Shank3-mutant mice lacking exon 9 show altered excitation/inhibition balance, enhanced rearing, and spatial memory deficit. Front Cell Neurosci 9: 94. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00094 |
| [119] | Lautz J, Zhu Z, Speed HE, et al. (2021) Shank3 mutations impair electrical synapse scaffolding and transmission in mouse brain. BioRxiv . https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.25.437056 |
| [120] |
Speed HE, Kouser M, Xuan Z, et al. (2015) Autism-Associated Insertion Mutation (InsG) of Shank3 Exon 21 Causes Impaired Synaptic Transmission and Behavioral Deficits. J Neurosci 35: 9648-9665. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3125-14.2015 
|
| [121] |
Jacot-Descombes S, Keshav NU, Dickstein DL, et al. (2020) Altered synaptic ultrastructure in the prefrontal cortex of Shank3-deficient rats. Mol Autism 11: 89. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.20698/v1 
|
| [122] |
Trobiani L, Meringolo M, Diamanti T, et al. (2020) The neuroligins and the synaptic pathway in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 119: 37-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.09.017 
|
| [123] |
Bazbaz W, Kartawy M, Hamoudi W, et al. (2024) The Role of Thioredoxin System in Shank3 Mouse Model of Autism. J Mol Neurosci 74: 90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02270-y 
|
| [124] |
Sauer AK, Bockmann J, Steinestel K, et al. (2019) Altered Intestinal Morphology and Microbiota Composition in the Autism Spectrum Disorders Associated SHANK3 Mouse Model. Int J Mol Sci 20: 2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092134 
|
| [125] |
Zhu F, Shi Q, Jiang Y, et al. (2024) Impaired synaptic function and hyperexcitability of the pyramidal neurons in the prefrontal cortex of autism-associated Shank3 mutant dogs. Mol Autism 15: 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-024-00587-4 
|
| [126] |
Jung S, Park M (2022) Shank postsynaptic scaffolding proteins in autism spectrum disorder: Mouse models and their dysfunctions in behaviors, synapses, and molecules. Pharmacol Res 182: 106340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106340 
|
| [127] |
Guang S, Pang N, Deng X, et al. (2018) Synaptopathology Involved in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 12: 470. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00470 
|
| [128] |
Auerbach BD, Osterweil EK, Bear MF (2011) Mutations causing syndromic autism define an axis of synaptic pathophysiology. Nature 480: 63-68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10658 
|
| [129] |
Pizzarelli R, Cherubini E (2011) Alterations of GABAergic Signaling in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neural Plast 2011: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/297153 
|
| [130] |
Jung H, Kim S, Ko J, et al. (2023) Intracellular signaling mechanisms that shape postsynaptic GABAergic synapses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 81: 102728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2023.102728 
|
| [131] |
Montanari M, Martella G, Bonsi P, et al. (2022) Autism Spectrum Disorder: Focus on Glutamatergic Neurotransmission. Int J Mol Sci 23: 3861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073861 
|
| [132] |
He JL, Oeltzschner G, Mikkelsen M, et al. (2021) Region-specific elevations of glutamate + glutamine correlate with the sensory symptoms of autism spectrum disorders. Transl Psychiatry 11: 411. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01525-1 
|
| [133] |
Schoonover KE, Dienel SJ, Holly Bazmi H, et al. (2024) Altered excitatory and inhibitory ionotropic receptor subunit expression in the cortical visuospatial working memory network in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 49: 1183-1192. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-024-01854-x 
|
| [134] | Hosseini H, Rodríguez Díaz JC, Pritchett DL, et al. (2024) Grin2a Hypofunction Disrupts Hippocampal Network Oscillations and E/I Balance Contributing to Cognitive Deficits. bioRxiv . https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.11.09.622809 |
| [135] |
Harrison PJ, Bannerman DM (2023) GRIN2A (NR2A): a gene contributing to glutamatergic involvement in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 28: 3568-3572. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02265-y 
|
| [136] |
Farsi Z, Nicolella A, Simmons SK, et al. (2022) Brain region-specific changes in neurons and glia and dysregulation of dopamine signaling in Grin2a mutant mice. Neuron 111: 3378-3396.e9. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.15.516665 
|
| [137] |
Lin KH, Hu TM, Hsu SH, et al. (2023) Identification of rare missense mutations in the glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit genes in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Genet 33: 20-25. https://doi.org/10.1097/ypg.0000000000000328 
|
| [138] |
Farsi Z, Sheng M (2023) Molecular mechanisms of schizophrenia: Insights from human genetics. Curr Opin Neurobiol 81: 102731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2023.102731 
|
| [139] |
Bai Y, Wang H, Li C (2022) SAPAP Scaffold Proteins: From Synaptic Function to Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cells 11: 3815. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233815 
|
| [140] |
Jaramillo TC, Speed HE, Xuan Z, et al. (2016) Altered Striatal Synaptic Function and Abnormal Behaviour in Shank3 Exon4-9 Deletion Mouse Model of Autism. Autism Res 9: 350-375. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1529 
|
| [141] |
Moutin E, Sakkaki S, Compan V, et al. (2021) Restoring glutamate receptosome dynamics at synapses rescues autism-like deficits in Shank3-deficient mice. Mol Psychiatry 26: 7596-7609. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01230-x 
|
| [142] |
Stasenko SV, Mikhaylov AN, Fedotov AA, et al. (2024) Astrocyte control bursting mode of spiking neuron network with memristor-implemented plasticity. Chaos Solitons Fractals 181: 114648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2024.114648 
|
| [143] |
Marcó De La Cruz B, Campos J, Molinaro A, et al. (2024) Liprin-α proteins are master regulators of human presynapse assembly. Nat Neurosci 27: 629-642. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-024-01592-9 
|
| [144] |
Waga C, Asano H, Sanagi T, et al. (2014) Identification of two novel Shank3 transcripts in the developing mouse neocortex. J Neurochem 128: 280-293. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12505 
|
| [145] |
Abedini SS, Akhavan S, Heng J, et al. (2023) A Critical Review of the Impact of Candidate Copy Number Variants on Autism Spectrum Disorders. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 794: 108509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2024.108509 
|
| [146] |
Lanovenko O (2021) Autistic spectrum disorders: genetic and epigenetic aspects. VLUBS 85: 3-17. https://doi.org/10.30970/vlubs.2021.85.01 
|
| [147] |
Havranek T, Bacova Z, Bakos J (2024) Oxytocin, GABA, and dopamine interplay in autism. Endocr Regul 58: 105-114. https://doi.org/10.2478/enr-2024-0012 
|
| [148] |
Rylaarsdam L, Guemez-Gamboa A (2019) Genetic Causes and Modifiers of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 13: 385. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00385 
|
| [149] |
Dimitrovski D, Stankovska G, Memedi I (2024) Genetic Aspects of Autism Spectrum Disorder. IOSR J Dent Med Sci 23: 57-60. https://doi.org/10.9790/0853-2309045760 
|
| [150] |
Paschou P, Fernandez TV, Sharp F, et al. (2013) Genetic susceptibility and neurotransmitters in Tourette syndrome. Int Rev Neurobiol 112: 155-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-411546-0.00006-8 
|
| [151] | Wang B, Li HH, Yue X, et al. (2018) A review on the role of γ-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway in autism spectrum disorder. Chin J Contemp Pediatr 20: 974-979. |
| [152] |
Choudhury PR, Lahiri S, Rajamma U (2012) Glutamate mediated signaling in the pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorders. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100: 841-849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2011.06.023 
|
| [153] |
Wang C, Wang H (2024) The growing challenge of autism spectrum disorder: a comprehensive review of etiology, diagnosis, and therapy in children. All Life 17: 2415057. https://doi.org/10.1080/26895293.2024.2415057 
|
| [154] |
Lim M, Carollo A, Dimitriou D, et al. (2022) Recent Developments in Autism Genetic Research: A Scientometric Review from 2018 to 2022. Genes 13: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091646 
|
| [155] |
Crittenden PM (2017) Formulating autism systemically: Part 1 – A review of the published literature and case assessments. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 22: 378-389. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359104517713241 
|
| [156] |
Legon W, Ai L, Bansal P, et al. (2018) Neuromodulation with single-element transcranial focused ultrasound in human thalamus. Hum Brain Mapp 39: 1995-2006. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23981 
|
| [157] | Al-Beltagi M, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS, et al. (2024) Decoding the genetic landscape of autism: A comprehensive review. World J Clin Pediatr 13: 98468. https://doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v13.i3.98468 |
| [158] |
Bedse G, Hill MN, Patel S (2020) 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Modulation of Anxiety and Stress Adaptation: From Grass Roots to Novel Therapeutics. Bio Psychiatry 88: 520-530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.01.015 
|
| [159] |
Cruz S, Zubizarreta SCP, Costa AD, et al. (2025) Is There a Bias Towards Males in the Diagnosis of Autism? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 35: 153-176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-023-09630-2 
|
| [160] |
Srinath S, Kalal A, Anand P, et al. (2025) Small SNPs, Big Effects: A Review of Single Nucleotide Variations and Polymorphisms in Key Genes Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int J Dev Neurosci 85: e70016. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdn.70016 
|
| [161] |
Marano M, Pilotto A, Padovani A, et al. (2024) The chronic use of serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors facilitates dyskinesia priming in early Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 271: 3711-3720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-024-12400-6 
|
| [162] |
Zhai S, Cui Q, Simmons DV, et al. (2023) Distributed dopaminergic signaling in the basal ganglia and its relationship to motor disability in Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 83: 102798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2023.102798 
|
| [163] |
Keltner NL (2005) Genomic Influences on Schizophrenia-Related Neurotransmitter Systems. J Nurs Scholarsh 37: 322-328. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2005.00056.x 
|
| [164] |
Forde NJ, Kanaan AS, Widomska J, et al. (2016) TS-EUROTRAIN: A European-Wide Investigation and Training Network on the Etiology and Pathophysiology of Gilles de la Tourette Syndrome. Front Neurosci 10: 384. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00384 
|
| [165] |
Chai A (2025) Pleiotropic neurotransmitters: neurotransmitter-receptor crosstalk regulates excitation-inhibition balance in social brain functions and pathologies. Front Neurosci 19: 1552145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2025.1552145 
|
| [166] |
Barrowman J, Wilson M (2023) Antidepressants and antipsychotics. Anaesth Intensive Care Med 24: 228-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpaic.2022.12.029 
|
| [167] |
Juhasz G, Gecse K, Baksa D (2023) Towards precision medicine in migraine: Recent therapeutic advances and potential biomarkers to understand heterogeneity and treatment response. Pharmacol Ther 250: 108523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108523 
|
| [168] |
Kang X, Wang D, Lin J, et al. (2024) Convergent Neuroimaging and Molecular Signatures in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease: A Data-Driven Meta-Analysis with N = 3,118. Neurosci Bull 40: 1274-1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-024-01218-x 
|
| [169] |
Katariya RA, Sammeta SS, Kale MB, et al. (2025) Agmatine as a novel intervention for Alzheimer's disease: Pathological insights and cognitive benefits. Ageing Res Rev 96: 102269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2024.102269 
|
| [170] |
Krishna G, Beitchman JA, Bromberg CE, et al. (2020) Approaches to Monitor Circuit Disruption after Traumatic Brain Injury: Frontiers in Preclinical Research. Int J Mol Sci 21: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020588 
|
| [171] |
Sun W, Liu SH, Wei XJ, et al. (2024) Potential of neuroimaging as a biomarker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: from structure to metabolism. J Neurol 271: 2238-2257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-024-12201-x 
|
| [172] |
Chruścicka-Smaga B, Machaczka A, Szewczyk B, et al. (2023) Interaction of hallucinogenic rapid-acting antidepressants with mGlu2/3 receptor ligands as a window for more effective therapies. Pharmacol Rep 75: 1341-1349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00547-4 
|
| [173] |
Rivera J, Sharma B, Torres MM, et al. (2023) Factors affecting the GABAergic synapse function in Alzheimer's disease: Focus on microRNAs. Ageing Res Rev 92: 102123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2023.102123 
|
| [174] |
Zhou X, Cheng Y, Zhang R, et al. (2017) Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist promotes retinal ganglion cell function via modulating GABAergic presynaptic activity in a chronic glaucomatous model. Sci Rep 7: 1734. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02092-6 
|
| [175] |
Pearl PL, Capp PK, Novotny EJ, et al. (2025) Inherited disorders of neurotransmitters in children and adults. Clin Biochem 38: 1051-1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2005.09.012 
|
| [176] |
Sun L, Wang Q, Ai J (2024) The underlying roles and neurobiological mechanisms of music-based intervention in Alzheimer's disease: A comprehensive review. Ageing Res Rev 96: 102265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2024.102265 
|
| [177] |
Brunet A, Stuart-Lopez G, Burg T, et al. (2020) Cortical Circuit Dysfunction as a Potential Driver of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front Neurosci 14: 363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00363 
|
| [178] |
Yadav A, Tadas M, Kale M, et al. (2025) Gut microbiota and behavioral ontogeny in autism spectrum disorder: a pathway to therapeutic innovations. Physiol Behav 299: 114989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2025.114989 
|
| [179] |
Li Q, Han Y, Dy ABC, et al. (2017) The Gut Microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 11: 120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00120 
|
| [180] |
Gonçalves CL, Doifode T, Rezende VL, et al. (2024) The many faces of microbiota-gut-brain axis in autism spectrum disorder. Life Sci 337: 122357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122357 
|
| [181] |
Borghi E, Vignoli A (2019) Rett Syndrome and Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders Share Common Changes in Gut Microbial Community: A Descriptive Review. Int J Mol Sci 20: 4160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174160 
|
| [182] |
Pedini G, Chen CL, Achsel T, et al. (2023) Cancer drug repurposing in autism spectrum disorder. Trends Pharmacol Sci 44: 963-977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2023.09.008 
|
| [183] |
Su Q, Wong OWH, Lu W, et al. (2024) Multikingdom and functional gut microbiota markers for autism spectrum disorder. Nat Microbiol 9: 2344-2355. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-024-01739-1 
|
| [184] |
Wan Y, Zhang L, Xu Z, et al. (2024) Alterations in fecal virome and bacteriome virome interplay in children with autism spectrum disorder. Cell Rep Med 5: 101409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101409 
|
| [185] |
Wu T, Wang H, Lu W, et al. (2020) Potential of gut microbiome for detection of autism spectrum disorder. Microb Pathog 149: 104568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104568 
|
| [186] |
Chen Q, Wu C, Xu J, et al. (2024) Donor-recipient intermicrobial interactions impact transfer of subspecies and fecal microbiota transplantation outcome. Cell Host Microbe 32: 349-365.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2024.01.013 
|
| [187] |
Suprunowicz M, Tomaszek N, Urbaniak A, et al. (2024) Between Dysbiosis, Maternal Immune Activation and Autism: Is There a Common Pathway?. Nutrients 16: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040549 
|
| [188] |
Schaepers-Cheu M, Patel M, Lien G, et al. (2024) Exploring the Gut Microbiome - Autism Spectrum Disorder Connection: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions and Future Directions. Berkeley Pharma Tech J Med 4: 34-58. https://doi.org/10.52243/bptjm.v4i1.54 
|
| [189] |
Nisar S, Bhat AA, Masoodi T, et al. (2022) Genetics of glutamate and its receptors in autism spectrum disorder. Mol Psychiatry 27: 2380-2392. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01506-w 
|
| [190] |
Zhao H, Mao X, Zhu C, et al. (2022) GABAergic System Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol 9: 781327. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.781327 
|
| [191] |
Rodriguez-Gomez DA, Garcia-Guaqueta DP, Charry-Sánchez JD, et al. (2021) A systematic review of common genetic variation and biological pathways in autism spectrum disorder. BMC Neurosci 22: 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-021-00662-z 
|
| [192] | Brix MK, Ersland L, Hugdahl K, et al. (2015) “Brain MR spectroscopy in autism spectrum disorder—the GABA excitatory/inhibitory imbalance theory revisited”. Front Hum Neurosci 9: 365. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00365 |